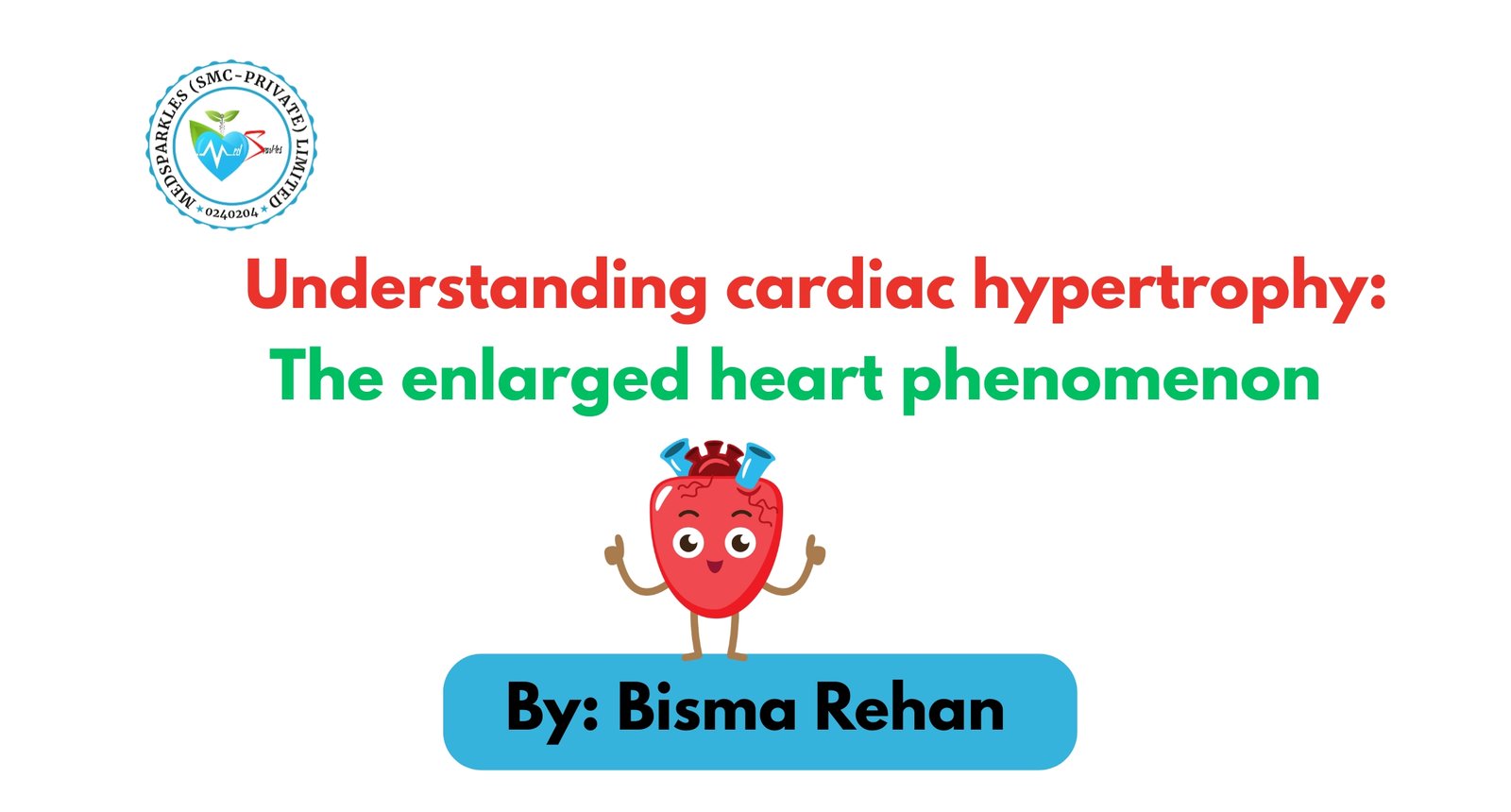
Introduction to Cardiac hypertrophy
Basically hypertrophy is a term that is characterized by an increase in the size of an organ because of the increase in cell size. Cardiac hypertrophy is a condition in which heart muscles (myocardium) become enlarged or simply defined as an increase in the size of heart muscles. It is an adaptation phenomenon, as the heart is exposed to stress or increased workload which in turn increases the size of heart muscles to pump blood effectively because of increased demand although prolonged excessive hypertrophy can lead to Heart complications. Cardiac hypertrophy is also referred to as ventricular hypertrophy because ventricle size increases. This condition cardiac hypertrophy can be both physiological and pathological (disease condition)
1. Physiological cardiac hypertrophy: It is considered a normal condition because it enhances cardiac function. It is most commonly seen in athletes. As athletes do a lot of exercises it increases the length of the myocyte (cardiac cells) or increases ventricle length and the workload on the heart increases because of exertion oxygen demand also increases so more blood get filled into the heart, and more blood is pumped out of the heart and more blood supply to the body.
2. Pathological cardiac hypertrophy: It is a condition that is characterized by the thickening of myocytes which results in decreased chamber size because of the increased width of myocytes, not length which ultimately reduces the capacity of the heart to fill up an adequate amount of blood and decreases the heart function so it doesn’t supply adequate amount of blood to body because of the shrinkage of chamber the workload on heart increases which raised the pressure on heart and due to prolonged stress the heart become pathologically hypertrophied.
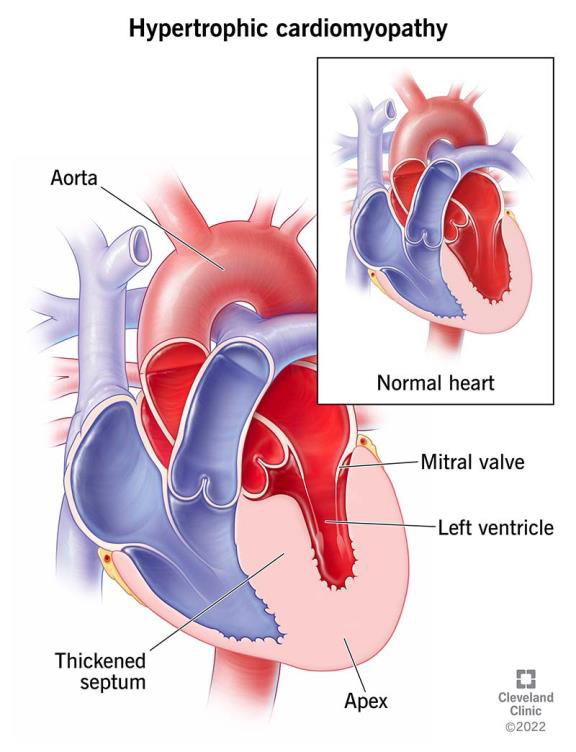
Right ventricular hypertrophy
As we have discussed earlier, hypertrophy is an enlargement of the heart muscle, so in this condition, the case is also similar that in right ventricular hypertrophy, the Right ventricle muscle mass becomes thickened as the chamber size
decreases because muscle thickness increases the pressure on the heart. There is a congenital heart defect called “Tetralogy of Fallot “and in this defect, the aorta is in the wrong position. The aorta shifted to the right side and it’s positioned above the hole in the heart wall. A hole in the heart wall means a ventricular septal defect in which a hole lies between the right and left ventricle, narrows the pulmonary Valve and thickens the right ventricle. As we know in a normal heart, the aorta is attached to the left ventricle. The oxygenated blood flow is proper throughout the body but in “Tetralogy of Fallot” as the aorta is between the right and left ventricle the blood flow is not proper or not even oxygenated which leads to cyanosis (bluish skin) and shortness of breath especially in infants.
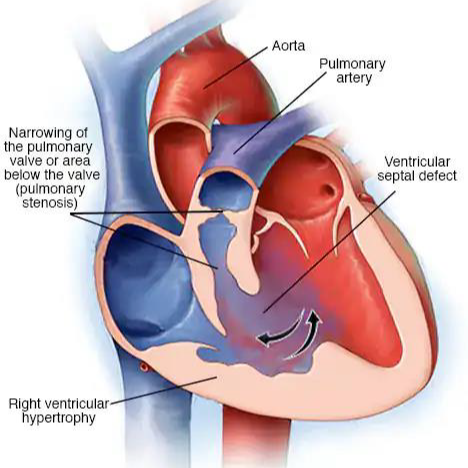
Common feature of Tetralogy of Fallot
The common feature of Tetralogy of Fallot is the “boot-shaped heart”. This is the radiographic finding that describes the shape of the heart on a chest X-ray where the heart is manifested as boot-shaped due to right ventricular hypertrophy as right ventricle becomes enlarged.
Causes of cardiac hypertrophy
The following are the factors that lead to cardiac hypertrophy,
1. Genetic Mutations: Hypertrophied cardiomyopathy can be a result of genetic mutations. The commonly involved genes MYH7, TNNT2 and TNNI3. The mutation in these genes causes the ventricles to become thickened and stiff which reduces the adequate blood supply.
2. Aging: As aging also affects our organs it can lead to cardiac hypertrophy. Let’s understand from an example that if blood pressure decreases the baroreceptors detect the low blood pressure and give a signal to CNS to produce such neurotransmitters that increase blood pressure. So in aging the body functions declined and don’t function properly which causes stress on the heart and the workload on the heart to increase which leads to cardiac hypertrophy.
3. Hypertension: Blood pressure not maintained leads to stress on the heart. Ultimately high blood pressure leads to more workload on the heart and it becomes harder for the heart to pump properly which increases the muscle mass and reduces chamber size leading to cardiac hypertrophy.
4. Long-term exercise: Athletes who are engaged in intense physical training can increase muscle length and develop cardiac hypertrophy.
5. Myocardial infarction: MI also known as a heart attack can lead to cardiac hypertrophy by compensatory mechanism. Due to myocardial infarction, the heart muscles get deprived of oxygen and this lack of oxygen leads to cardiac muscle cell death. So to maintain the heart function the healthy cardiac cell undergoes compensatory changes that is cardiac hypertrophy where heart muscles thicken or enlarge.
Symptoms of cardiac hypertrophy
Following are the symptoms of cardiac hypertrophy
1. Chest pain: it occurs as a result of increased stress on the heart which reduces blood supply towards the heart muscle making the individual experience chest pain or angina.
2. Palpitations: Because of the increased workload on the heart it results in an irregular heartbeat.
3. Shortness of breath: As heart chamber size decreases there is no adequate blood filling up in the heart so no proper blood supply leading to stress on heart which decreases the pumping efficiency of the heart and results in shortness of breath.
4. Fainting: During prolonged exercise or in severe cases when there is decreased blood supply it leads to dizziness or fainting, especially after physical exercise.
Diagnosis of cardiac hypertrophy
The diagnosis of cardiac hypertrophy can be done by several methods and tests by checking medical reports or the history of the patient. For examination following dominant tests are used
1. Echocardiogram: This test is the most reliable and it provides detailed information on heart structure and its function makes it easier for healthcare providers to professionally visualize the size of the heart Chambers, how accurately the heart muscle is working what’s their thickness and how well the heart pumps it’s all can diagnose by echocardiogram with the help of sound waves or ultrasound scanning.
2. Electrocardiograph: If we talk about electrocardiograph, as the name suggests electro means this test helps conduct or record the electrical activity of the heart by electrical waves and shows the heart rhythm and abnormalities that occur in the electrical conduction system. As an electrocardiograph tells about irregular heart rhythm, not about the physical structure or anatomy of the heart so echocardiogram is more reliable.
Treatment
Cardiac hypertrophy if left untreated leads to several complications one of the complication is heart failure so it is necessary to treat this. Treatment for cardiac hypertrophy is important because It manages the underlying causes and prevents complications by improving quality of life. Treatment options include are
1. Medications: Medicines like beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers help to reduce the heart rate and reduce muscle stress so in that way the heart can pump easily which can manage blood pressure and arrhythmias.
2. Septal myectomy: It is a surgical intervention in which the excessively grown wall between the heart Chambers and this wall is called septum can be removed by surgery which ultimately improves the blood flow from the heart. The surgeon also locates the thickened heart muscle that can be removed via surgery.
3. Lifestyle changes: lifestyle changes play a pivotal role in managing or improving heart risk and promoting heart health. This includes maintenance of a balanced diet, engaging yourself in moderate or regular exercise or quitting smoking these all factors contribute towards cardiovascular health.
4. Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of your blood pressure and follow-up with the cardiologist is essential to adjust or manage the condition.
5. Heart transplant: This is the last option when if no treatment plan occurs so the diseased heart is transplanted with a healthy heart.
Conclusion
Cardiac hypertrophy is a complex condition because it is related to the heart. As we know our heart is the most important organ that supplies blood throughout the body through the aorta but if any unnecessary change occurs in our heart like the cardiac hypertrophy we have discussed, it leads to many severe complications such as heart failure if not treated because of cardiac hypertrophy the muscle chamber size decrease which leads to decrease filling of blood and results in decrease supply of blood, as a coronary artery that supplies blood back to the heart for the proper functioning of heart, but if the heart is not functioning better because of low blood supply it leads to heart failure. It’s necessary to understand the complications of cardiac hypertrophy so we can choose the best options for treatment because cardiovascular health is the top priority for living an active life.
FAQS
Q1: What is cardiac hypertrophy?
Cardiac hypertrophy is a condition of enlarged heart phenomenon where the heart muscle becomes thicker and abnormal in response to stress and increase work load.
Q2: What are the causes cardiac of hypertrophy?
It can be both pathologically and physiologically. Whereas common causes include genetic mutation, hypertension, aging, long term exercise and MI.
Q3: What are the symptoms of cardiac hypertrophy?
Common symptoms are shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, dizziness, and heart palpitations.
Q4: How is cardiac hypertrophy diagnosed?
It can be diagnosed commonly by echocardiogram and electrodiograph.
Q5:Can cardiac hypertrophy be treated?
It can be treated by lifestyle changes, septal myectomy, regular monitoring with proper intake of medicine, and heart transplant.
REFERENCE