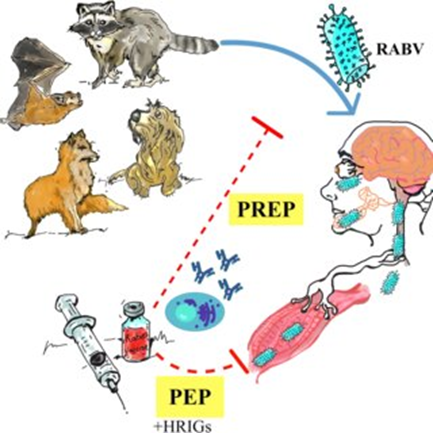
Rabies is a virus that affects the Central nervous system (CNS). Once clinical symptoms appear, rabies is nearly always fatal. Humans contract it mostly from the bite or scratch of an infected animal, usually a dog, although it can also spread to bats, raccoons, and other wild animals. The prevention of rabies after exposure is vital because of its high mortality rate. When properly and immediately delivered, Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) is a life-saving medical treatment that can stop the onset of this fatal illness.
What is PEP?
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) is a series of medical treatments given after a potential exposure to the rabies virus to prevent a fatal disease from occurring. PEP is a highly effective method and should be initiated as soon as possible after an exposure. It can be given through:
- Wound Care: The Immediate and proper cleaning of the wound is the first and most crucial step. The wound should be washed vigorously with soap and water for at least 15 minutes. This physical cleansing helps remove the virus from the bite site.
- Rabies Immunoglobulin (RIG): There is an antibody preparation that offers quick, temporary defense against the rabies virus. The area surrounding the wound was directly injected with RIG. Before the immune system can react to the vaccine, these antibodies neutralize the virus.
- Rabies Vaccine: A series of vaccines is administered to encourage the body’s immune system to create its own antibodies against the virus. Vaccination is usually administered over a few days or weeks in a series of doses. The vaccination protocol determines the number of doses and the timing of the vaccinations.
Importance of PEP
The significance of PEP cannot be overstated. After exposure, this is the only way to prevent rabies.
- Effectiveness in Preventing Rabies: PEP is almost 100% effective in preventing rabies when administered promptly and correctly. This makes it an essential intervention for anyone who has been bitten or scratched by an animal thought to be rabid.
- Time Sensitivity and Prompt Administration: Efficacy of PEP is extremely time-sensitive. The likelihood of a successful outcome increases with the timing of treatment initiation following exposure. Although 24-48 hours is the optimal window, PEP can still be effective if started later because rabies can have a lengthy incubation period. Any delay raises the possibility that the virus will infect the central nervous system.
Conclusion:
Overall, Rabies is a fatal disease, but it can also be prevented through timely and effective post-exposure prophylaxis. In Pakistan, where rabies remains a significant public health threat, access to and awareness of PEP are critical. While challenges like the availability and cost of the vaccine and RIG may exist, everyone needs to be aware of the importance of PEP. By understanding the lifesaving nature of PEP, we can work towards reducing the burden of rabies and moving closer to a future where this deadly disease is no longer a threat.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What should I do immediately after being bitten by an animal?
The wound should be washed well for at least 15 minutes with soap and water immediately. This is an important step that can considerably lower the risk of infection. Seek medical help immediately, preferably at a clinic or hospital that offers PEP. Applying anything to the wound other than soap and water is not recommended.
How effective is PEP in preventing rabies infection?
PEP, which includes the whole series of rabies vaccines, the injection of rabies immunoglobulin (RIG) into the wound, and appropriate wound care, is almost 100% successful in preventing rabies if given promptly and correctly. The effectiveness of the entire course of treatment may be jeopardized if it is not completed.
When should PEP be initiated after exposure?
After exposure, PEP should be initiated as soon as feasible, preferably within the first 24–48 h. However, because rabies can take a long time to incubate, PEP can still be effective even if it is initiated weeks or months after exposure. The most important thing is to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Where can I access PEP in Pakistan?
Public and private major hospitals in Pakistan’s cities usually offer PEP treatment. For instance, hospitals in Islamabad, Lahore, and Karachi are well-equipped. You can also ask your local health authority or healthcare professional for a list of local rabies treatment facilities.
Is PEP covered by health insurance in Pakistan?
In Pakistan, PEP coverage varies greatly among health insurance plans. In the event of an unintentional injury, certain private health insurance plans may cover all or part of the expenses. To determine how PEP and emergency medical treatment are covered under your policy, it is strongly advised that you contact your insurance company. Sometimes, people who cannot afford treatment can get help from government programs or nonprofits.