What is Stress?
Stress refers to a natural response of your organism to a problem or pressure. When the brain believes that it requires additional energy or attention, it
activates a warning mode in your brain to enable you to handle it. This is natural and even beneficial (e.g., to satisfy a deadline). It is an issue when it is too intense, too frequent, or too protracted.
How does stress look/feel?
View stress as an indicator in four directions, including body, emotion, thoughts, and actions.
| Area | What you might notice (examples) |
| Body | Tight shoulders/neck, headaches, fast heartbeat, sweating, upset stomach, tiredness, shallow breathing, trouble sleeping |
| Emotions | Feeling anxious, irritable, overwhelmed, moody, and low motivation |
| Thoughts | Racing thoughts, overthinking, “I can’t do this,” difficulty focusing or remembering |
| Actions | Procrastination, snapping at people, eating too much/too little, scrolling a lot, avoiding tasks, more caffeine/smoking |
Determine the triggers of stress in your life
The process of stress management begins with determining the causes of stress in your life. This does not sound as simple as it might seem. Although it is not hard to name the biggest sources of stress that include as changing a job, moving, or getting a divorce, it might be more difficult to define the causes of chronic stress.
It is so easy to forget about the role that your thoughts, feelings, and actions play in causing your daily stress. Of course, you can be aware that you are under constant pressure of work deadlines, but perhaps it is your procrastination that is causing the stress and not the job itself.
Practicing the 4As of Stress Management
One can reduce stress or deal with its effects through a lot of healthy ways, but they all involve the process of change. The situation can either be changed, or your response can be changed. It is always good to consider the four as of avoid, alter, accept, and adapt when making decisions between two possible options.
Avoid Unnecessary Stress
Although certain stressors cannot be avoided, several stressors may be done away with:
- Say no – know your boundaries and target.
- Duck stressful individuals – restrict the time or terminate unproductive relationships.
- Manage the setting- modify what causes anxiety (e.g., do not turn on the news, go online shopping, use less stressful routes).
- Avoid hot-button issues – avoid discussions that keep one person at loggerheads.
- Reduce the items on your list to-do – distinguish between what you must do and what you should do, and eliminate things that you do not need to do
Alter the Situation
When you cannot avoid stress, deal with it differently:
- Be expressive – speak out about all issues in a respectful manner.
- Compromise – be adaptable such that both parties can reach a compromise.
- Be demanding – solve problems and establish boundaries.
- Finding balance – work and relaxation, social life and solitude, to avoid burnout.
Adapt to the Stressor
You can’t alter the stressor: alter your reaction:
- Restate problems – view them positively or neutrally.
- See the big picture — will it have any lasting value in the long run? Then ditch it.
- Reduce standards – do not be a perfectionist; tolerate good enough.
- Be thankful – look at what you are thankful about to maintain perspective.
Accept What You Can’t Change
Some stressors are beyond our control, and, therefore, we should accept them:
- Quit attempting to govern the ungovernable – concentrate on how you respond to it.
- See the positive side – use hardships as learning moments.
- Forgive- Repent and forget anger and resentment to free up negative energy.
- Sharing feelings, confiding in someone you can trust, or a therapist can be a relief.
Tips and Techniques to Release Stress
Different stress management techniques and strategies are not effective for all people and in all scenarios, and thus, experiment. Pay attention to things that make you feel relaxed and control yourself.
Deep breathing and mindfulness:
Mindfulness Meditation:
- Sitting Meditation: Sitting comfortably with eyes closed and concentrating on the breath, and when the mind strays, it is necessary to draw attention back to the breath.
- Body scan: Being lying down, one should pay attention to the various parts of the body without any judgment.
Mindful Breathing: This involves slow, deep breathing where the only thing that you do is feel yourself breathing.
Mindful Walking: Walking mindfully, taking time, and focusing on the movement of the body and the experience of walking.
Mindful Eating: It involves eating slowly and fully cherishing every bite of food and being fully engaged in the task of eating.
Informal Practices: A person can also be mindful even when engaging in daily life activities, like washing dishes, driving, or having a conversation.
Meditation
Meditative Concentration:
Technique: Sit down and pay attention to your breath. Experience the feeling of air being in and out of your nostrils or your stomach coming up and down. In case your mind is not focused, shift it back to the breath.
Duration: It should be 5-10 minutes at the start of the day, when you will feel more at ease, and then you can add more time.
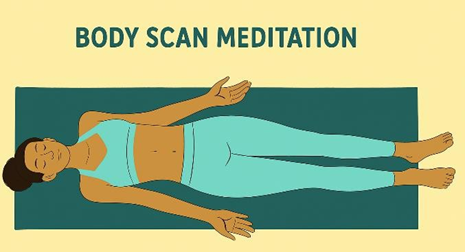
Body Scan Meditation:
Technique: Lie on your back, keep your legs straight, keep your arms straight (at your side), keep the palms facing up. Slowly and intentionally concentrate your attention on every part of your body, starting with the toes to the head or vice versa.
Duration: This may be carried out between 20-45 minutes.
Mindfulness Meditation:
Technique: Sit comfortably. Shut your eyes and give your attention to your breathing. Accept thinking and letting thoughts come and go without evaluation, and put your mind in your breath when it slips.
Duration: 10-15 minutes per day is a good beginning.
Physical Activity
The last thing that you do want to do when you are stressed is to get up and exercise. However, physical activity is a tremendous stress reliever- and you do not need to be a sportsman or spend hours in the gym to feel the difference. Exercise also releases endorphins that help you to feel good, and can also be a good way to forget about your daily stresses.
Although you will be doing yourself a favor by committing to exercising at least 30 and above- minutes regularly, there is nothing wrong with easing into the process of conditioning yourself. Even the smallest activities may accumulate during a day. The initial one is to get yourself up and moving. These are some of the simple methods to add exercise to your daily routine:
- Play some music and dance about.
- Take your dog for a walk.
- Use walking/cycling to the grocery store.
- Use stairs at home or the place of work instead of using the elevator.
- Park in the least loved area of the parking lot and walk to the rest.
Breathing Techniques

Deep Breathing Technique: Sit or lie in an easy posture.
Put one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest. Inhale deeply using both nose and lungs, and this time the diaphragm (not the chest) gets inflated with sufficient air to produce a stretch in the lungs. Breathe out slowly via mouth.
Duration: 5-10 minutes.
4-7-8 Breathing:
Procedure: Lie or sit in a comfortable position. Breathe in silently (with your nose) 4 times. Count to 7 and hold your breath. Breathe out totally using the mouth, making a whoosh sound, counting to 8. Time: Repeat the cycle 4 times.
Box Breathing (Square Breathing):
Posture: Sit in an erect position. Breathe in slowly, counting to 4 with your nose. Count to 4 while holding your breath. Breathe out 4 times using the mouth. Breathe again, count of 4.
Time: Duration of 5 minutes.
Alternate Nostril Breathing:
Technique: Sit comfortably. Close your right nostril with your right thumb. Breathe deeply in through your left.
Lifestyle Habits
- Give Self-Care the First Priority: You should get time to do things you like that would help you relax and re-energize, such as reading, gardening, or listening to music.
- Healthy Diet: Have a balanced diet and minimize overconsumption of caffeine and sugar, as well as processed foods, which aggravate stress.
- Good Sleep: Maintain a sleep routine and a bedtime ritual that will help you to maintain mental and physical well-being.
- Limit Stressors: Learn to reduce your exposure to stressors by cutting down on excess screen time, news, and social media.

Time Management and Prioritization
Time management and prioritization will assist in eliminating stress, enhancing well-being through planning and scheduling activities, goals, and time management. Key strategies include:
- Prepare a daily to-do list: Be able to list tasks daily, write the large ones down into sub-tasks, and rank by urgency and importance to be focused and organized.
- Be SMART: Set goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound to ensure that the goals are clear and realistic.
- Eisenhower Matrix: classify tasks into four quadrants, that is, urgent/important, important/not urgent, urgent/not important, and none. Consider the first two, outsource or discontinue the rest.
- Plan frequent breaks: Take brief breaks so that you do not burn out, but stay focused, and then take a break by walking, breathing deeply, or taking a rest.
- Create habits: Develop regular practices in life (e.g., meals, exercise, sleep) so that you bring some organization into your life and can more effectively manage time.
- Outsource and say no: Divide and conquer where it makes sense and reject demands that would not fit your agenda or cause you stress.
- Reduce multitasking: To be more productive and less stressed, do one thing at a time.
- Make use of time management tools: Use calendars, planners, or apps to organize tasks, create reminders, and keep track of progress.
- Reflect and reassess: You need to revisit your strategies regularly and readjust them to achieve productivity and balance between work and life.
Conclusion
Stress can be described as a natural reaction to situations that are challenging to deal with, yet it may harm mental, emotional, and physical health when unattended. The knowledge of stress and coping strategies will play a crucial role in keeping a balance and resilience. In response to the stressors, 4 As of stress management: Avoid, Alter, Adapt, Accept; provide a practical model on how to deal with the situation by changing it or altering the reaction to it. Coupled with this, the inclusion of evidence-based methods like meditation and mindfulness and breathing exercises would calm down the mind, reduce anxiety, and enhance concentration. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, proper nutrition, proper sleep, and fostering social relationships are also beneficial in promoting overall well-being. Further, negatively, good time management and prioritization to achieve a goal, a set of routines, breaks, delegation, and tools can help one feel less overwhelmed and lead a more balanced day. Through such a combination, one will be able to develop healthier reactions to stress, develop a stronger emotional base, and train a more focused, productive, and peaceful state of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the typical signs and symptoms of stress?
It may be emotional (e.g., irritability, anxiety, mood swings), mental (poor focus, racing thoughts), physical (e.g., headache, tiredness, muscle tension), and behavioral (e.g., sleeping problems, overeating, withdrawal).
- What can the students do to cope with academic stress?
Time management, setting realistic goals, taking regular breaks, healthy habits, peer support, and relaxation methods such as mindfulness are some of the methods students can use to manage the pressure of studying and have balance.
- Is it possible to eliminate stress?
No, it is impossible to get completely rid of stress since it is the nature of things. Nevertheless, it can be addressed successfully by using healthy coping skills, changing attitude and lifestyle to reduce its impact on it.
- What is the time period of stress management techniques to cause results?
The time is dependent on the individual and the method. Certain techniques, such as deep breathing, provide instantaneous relief, whereas other techniques, such as meditation, mindfulness and changing lifestyles, provide slow gains over weeks when performed regularly.
- What should one do in case stress is overwhelming, even with the methods?
Stress can be temporary and easy to manage; however, it can be chronic and overwhelming, and therefore, professional assistance from a therapist, counselor, or doctor can help. The individualized coping skills and emotional support may be provided through professional guidance.
References
- https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=n08WEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP9 &dq=Managing+stress+in+a+fast+paced+world:+Tips+and+techniques&ots=O8lCbYM
_zb&sig=Z36ExGOEM49oIVViCBqAD_-uCAc&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false






