The hemoglobin count is one of the main results analyzed in blood tests. And no wonder, since it is one of the most important proteins in the body. Hemoglobin is essential for each of the body’s organs to receive the amount of oxygen needed to perform their functions. In addition, it also has the function of carrying carbon dioxide to the lungs, which is then expelled.
If hemoglobin levels drop, oxygen uptake also drops. That’s why it’s so important to keep it at optimal levels. On this occasion, we’ll tell you at One that what the causes of low hemoglobin are , as well as the symptoms and treatments that are usually followed to increase it. If you suspect that you have a low hemoglobin count, don’t hesitate to go to the doctor so that he can tell you the right treatment to follow.
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. It is important because if hemoglobin levels drop, the body does not receive the oxygen it needs. This is how anemia occurs.
What is low hemoglobin?
Each red blood cell contains hemoglobin. In fact, hemoglobin is what gives blood its characteristic red color. It is an iron-rich protein to which oxygen and carbon dioxide attach themselves in order to travel throughout the body. So, what is low hemoglobin? It is what happens when, when performing a blood test, the hemoglobin values in the blood are lower than those considered normal.
What happens when hemoglobin drops?

Fatigue. Dizziness. Rapid heart rate. All of these signs could be signals of anemia due to low hemoglobin . In fact, it is a fairly widespread problem in Peru and on the planet. According to the WHO, a quarter of the world’s population suffers from anemia.
This blood disorder can affect the health and quality of life of those who suffer from it. It can occur during pregnancy, as a result of heavy bleeding, or due to acquired or hereditary health problems.
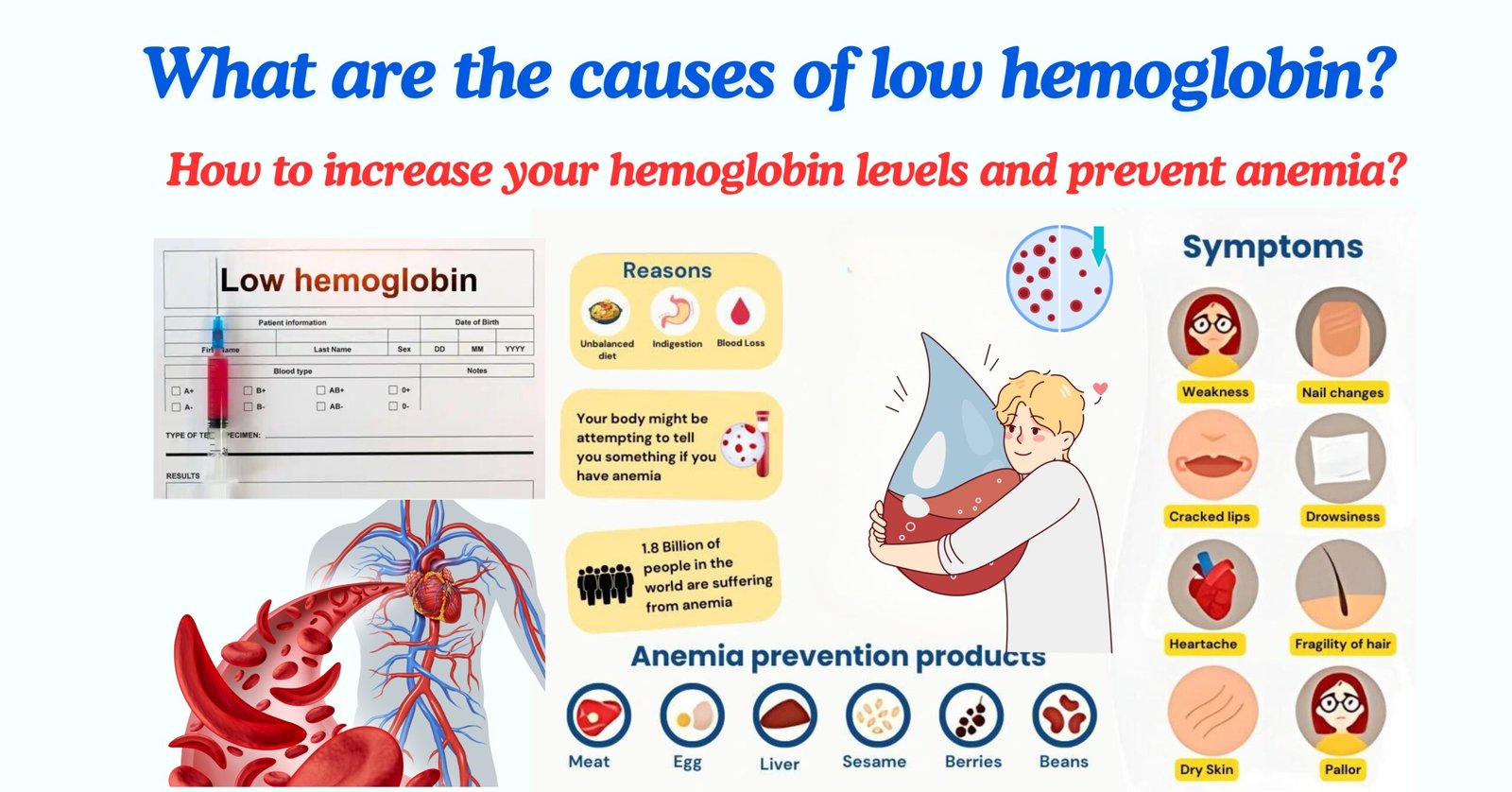
The causes of low hemoglobin levels are very varied and often coexist in the same patient. One of the possible causes of anemia is leukemia or blood cancer.
But the most common cause is iron deficiency in the diet, known as iron deficiency anaemia. This type of condition is associated with learning difficulties and decreased cognitive ability. These are, precisely, the main risks of low haemoglobin .
Fortunately, low hemoglobin levels can be successfully treated and prevention is possible at any age. You just need to know the symptoms of low hemoglobin levels for anemia and follow some dietary tips . Keep reading!
Symptoms and signs of low hemoglobin

There are several possible signs of anemia that often coexist in the patient. It is worth mentioning that sometimes a symptom as curious as it is rare is observed: the need to consume inedible substances, such as pieces of wall or plaster, earth or mud.
Typically, the most common ones are:
- Tiredness or weakness for no apparent reason.
- Paleness, yellowish skin and eyes.
- Dizziness or vertigo.
- Discouragement or bad mood.
- Excessive thirst.
- Dark tea-colored urine.
- Sweating.
- Symptoms of heart problems (rapid heart rate, weak pulse, murmurs, heart failure, etc.).
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing.
- Cramps in the lower legs.
How much iron does the body need?
There are several factors that determine how much iron a body needs to maintain high hemoglobin levels. Each person’s particular needs, iron loss, and diet, among other factors, must be taken into account.
For example, according to the FAO, a normal person only absorbs 10% of the iron from the food consumed. Thus, an adult man can lose between 0.5 and 1 mg of iron per day; therefore, his daily iron requirement is approximately 10 mg.
On the other hand, an adult woman before menopause loses almost twice as much iron as a man. This does not take into account that during childbirth and breastfeeding there is also a significant loss of iron.
Finally, babies – and some growing children – need additional iron in their diet. Therefore, it is always best to consult a doctor to determine the amount of iron needed in each case.
Similarly, the amount of iron that can be assimilated from each food varies greatly. As a general rule, iron from animals, i.e. meat, chicken and fish, is well absorbed. The same does not happen with iron from plant sources such as wheat, rice and corn, for example.
In fact, according to the FAO, plant-based iron is poorly utilized by the body. However, this situation can be reversed by combining certain foods. Below are five nutritious recipes and some dietary tips on how to keep hemoglobin high .
Hemoglobin: normal values
Although each laboratory has its own standards, these never differ much from each other. Hemoglobin results are located in the hemogram , a test where the concentration of blood cells, such as erythrocytes and leukocytes, is analyzed. Generally, the normal hemoglobin level varies depending on the sex and age of the patient. Normal hemoglobin values range between [1] :
- Women : 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL.
- Pregnant women : 11.0 g/dL or higher.
- Men : 13.8 to 17.2 g/dL.
- Children between 6 months and 4 years : 11 g/dL or higher.
- Children between 5 and 11 years : 11.5 g/dL or higher.
- Children between 12 and 14 years : 12 g/dL or higher.
Low hemoglobin: consequences
What happens if hemoglobin levels are lower than normal? There are certain situations, such as menstruation or pregnancy, that can cause a drop in hemoglobin levels. As we have seen, low hemoglobin levels during pregnancy are to be expected. Small drops do not necessarily have to scare us, but it is always advisable for a doctor to evaluate the condition and circumstances of each patient.
However, significantly low hemoglobin is a health risk. The body is not receiving the oxygen it needs to function and the body’s energy is affected. This condition, which causes red blood cells to become diseased, is commonly known as anemia.
Untreated anemia can have short- and long-term consequences. In children, physical and psychological development can be seriously affected, since oxygen allows for optimal growth of organs and the body. In older people, studies have shown that low hemoglobin increases the risk of suffering from dementia.
In everyday life, a lack of hemoglobin can cause extreme fatigue and an inability to carry out daily activities. If anemia reaches a very severe level, the heart must pump blood much harder to compensate for the lack of oxygen. Eventually, this can lead to heart failure and even death
Low hemoglobin: causes
What causes the body to stop producing the hemoglobin it needs? There can be many causes of low hemoglobin, but the most common of them is a lack of iron, folic acid or B vitamins, such as vitamin B12 and B6. These chemicals are necessary for the creation of new red blood cells and a deficit in their consumption can result in an alteration of the normal levels of hemoglobin.
Low hemoglobin due to lack of nutrients
Low hemoglobin caused by a lack of iron is called iron deficiency anemia . This can occur because the patient does not consume enough iron-rich foods or because the body fails to absorb the iron it ingests. The latter can be due to intestinal disorders such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
On the other hand, a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 can cause megaloblastic anemia, a type of anemia characterized by deformed and larger than normal red blood cells. In these cases, the composition of red blood cells does not develop completely and their life expectancy is reduced.
Low hemoglobin due to blood loss
Blood loss is also one of the causes of low hemoglobin. There is no need to suffer from external injuries or trauma, as blood loss often goes unnoticed because the bleeding is internal. Conditions such as ulcers, bleeding from the urinary tract or hemorrhoids are examples of internal blood loss.
Low hemoglobin due to bone marrow disorders
The body produces red blood cells and hemoglobin in the bone marrow. Therefore, bone marrow disorders or injuries can also be behind the reason for low hemoglobin levels. This type of condition is called aplastic anemia and can also occur as a result of immune system disorders, in which the body itself attacks the production of blood cells.
Other causes, such as exposure to radiation, excessive use of certain drugs, such as chloramphenicol, or pregnancy can trigger blood defects.
Low hemoglobin due to chronic diseases
In chronic diseases, hemoglobin levels can drop due to inflammation. This can slow down red blood cell production, reduce their lifespan, and even change the way the body uses iron. Conditions that can lead to this type of anemia include rheumatoid arthritis, viruses such as hepatitis or HIV/AIDS, cancer, lupus, lymphoma, and others.
Low hemoglobin due to other diseases
Less common diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, can cause low hemoglobin. In these circumstances, red blood cells are defective from the moment they are created. They break and die easily, causing a deficit in the amount of oxygen the body needs.
On the other hand, blood porphyria, a rare hereditary disorder, includes a group of diseases characterized by the body’s failure to produce heme, an elementary component of hemoglobin.
Low hemoglobin: medical treatment
Treatment for low blood hemoglobin will depend on the cause of the body’s loss of hemoglobin in the first place. Because anemia is mostly caused by iron deficiency, the most common treatment is to prescribe nutritional supplements and a balanced diet that includes the vitamins and minerals needed for proper blood cell function.
If low hemoglobin is caused by other diseases, medications will be prescribed to help combat them. This is the case for immune disorders that cause the body to attack its own red blood cells, or infections for which antibiotics are prescribed. In the case of excessive menstrual bleeding, it is common to prescribe hormones to reduce the amount of blood lost during each menstruation.
For bone marrow disorders, stem cell or bone marrow transplantation may be an option for patients suffering from diseases that otherwise have no cure.
If the anemia is very severe and requires immediate treatment, doctors may choose to perform a blood transfusion. This scenario can occur in cases where the patient has hemoglobin at 7 or below, which is dangerous.
How to increase hemoglobin naturally
When anemia is due to a deficiency in iron, vitamins or folic acid, it is recommended to follow a more balanced diet that helps bring hemoglobin and red blood cell levels back to normal. Some of these foods to raise hemoglobin include green leafy vegetables such as spinach and broccoli, nuts, whole grains, oily fish such as sardines and anchovies, legumes and beef, chicken, pork and turkey.
Vitamin C is a great ally for raising hemoglobin naturally, as it helps the body effectively absorb the iron it has consumed. Thus, foods rich in vitamin C should also be included in the diet. Citrus fruits, such as red berries, oranges or kiwi, are known for their high vitamin C content. Likewise, vegetables such as peppers and carrots fall into the same category.
B vitamins can be found in dairy products, meats and seafood, while foods such as bananas, papaya, liver and asparagus contain folic acid.
If, on the other hand, the blood test shows a high hemoglobin level , the doctor may recommend reducing the intake of iron-rich foods.
Foods to increase hemoglobin
1. Lentil salad
Ingredients:
- 225 g of cooked lentils
- 2 cloves of garlic
- ¼ teaspoon cumin
- 1 tablespoon of each of the following chopped foods (or other foods of your choice): cucumber, pepper, celery, tomato, radishes, avocado and onion
- 1 tablespoon of cilantro leaves
- Lemon juice to taste
- Olive oil to taste
- Salt and pepper to taste
Preparation:
Cook the lentils for 12 minutes in water with the 2 cloves of garlic and ¼ teaspoon of cumin. Once ready, strain the lentils and mix them with the chopped ingredients (cucumber, tomato, avocado, etc.). Add cilantro leaves, olive oil, lemon juice, salt and pepper to taste; mix and serve.

2. Blood sausage burger
Ingredients:
- 200 g. of chicken blood
- 100 g. ground beef
- 100 g. quinoa flour
- 2 spinach leaves
- 2/3 cloves of garlic
- 80 cc. Vegetable oil
- 100 cc. Of water
Preparation:
Boil the blood sausage and chop it into small squares. Dissolve the quinoa flour in half a cup of water. Add the spinach and chopped garlic, the blood sausage and the meat. Mix well, adding salt to taste. Divide into portions and place on a hot grill.
3. Homemade pate
Ingredients:
- 500 grams of chicken liver
- 250 grams of Onion
- 100 grams of butter
- 12 units of whole black pepper
- 1 sprig of Thyme
- 1 pinch of ground pepper
- 1 piece of Salt
Preparation:
Grate the onions, clean the chicken livers, wash and dry them to prepare the homemade pâté.
Melt the butter in a pan. Once melted, lower the heat and fry the onion in it until it becomes transparent.
Add the finely chopped chicken livers, thyme and ground pepper to taste to season the pate. Let it simmer for a few minutes.
Once the above ingredients are ready, process them with a blender, food processor or electric mixer until you obtain a paste. Add the peppercorns, mix again and leave the preparation in the refrigerator for at least 8 hours

Important sources of iron in the body
Eating iron-rich foods is important to keep hemoglobin levels high. However, it is also very important to learn how to combine them to enhance the absorption of the mineral. Here are some ideas:
- Meats with vegetables . This is the combination par excellence, as it combines the iron from animal protein with the vitamin C from vegetables. This vitamin helps improve the absorption of the mineral. Combine them with parsley, peppers or tomatoes, and/or a dessert of strawberries, kiwi, mango, pineapple or papaya . All of them contain large amounts of vitamin C.
- Daily snack of nuts. A handful of pistachios, almonds and walnuts provide an extra amount of iron and other important minerals.

What foods should we avoid to maintain high hemoglobin levels?
On the other hand, it is also important to avoid certain food combinations that reduce the assimilation of the mineral in the body. These combinations do not help to maintain high hemoglobin levels. Here are some tips:
- Dairy products are best eaten between meals. Avoid eating foods with calcium (or supplements) during meals because they can compete with iron absorption.
- Coffee and tea , one hour after meals. Their high tannate content reduces the assimilation of iron in the body. It is best to drink them at least one hour after eating; the same goes for caffeinated soft drinks.
- Beware of additives. Soft drinks and fizzy drinks contain phosphates among their additives, which can complicate the use of iron and cause a drop in hemoglobin.
- Cereal and iron separately. Phytates and phosphates contained in cereal grains are potential inhibitors of iron absorption. It is best to consume them separately.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing hemoglobin levels is crucial for maintaining good health. Low hemoglobin, often indicative of anemia , can result from various factors including nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, blood loss, and bone marrow disorders. The blog discusses the importance of hemoglobin, a key protein in red blood cells responsible for oxygen transport throughout the body. It highlights common symptoms of low hemoglobin such as fatigue, paleness, and rapid heart rate, which signal the need for medical evaluation and possibly dietary adjustments.To combat low hemoglobin, the blog recommends incorporating iron-rich foods like leafy greens, meats, and legumes into one’s diet, alongside vitamin C to enhance iron absorption. It also advises on foods to avoid that may hinder iron uptake. For severe cases, medical treatments such as supplements, medications, or even transfusions may be necessary. By understanding the causes and embracing both dietary and medical solutions, individuals can effectively manage their hemoglobin levels and improve their overall health



1 Comment.