Managing insulin therapy can feel overwhelming at first, but breaking it down into clear, manageable steps makes it easier to handle. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you get started with an insulin regimen:
Step 1: Understand the Different Types of Insulin
- Rapid-acting insulin: Starts working within 15 minutes and lasts about 2-4 hours. It’s usually taken just before meals.
- Short-acting (regular) insulin: Kicks in after about 30 minutes and lasts 3-6 hours, also taken before meals.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: Begins working in 2-4 hours and can last 12-18 hours.
- Long-acting insulin: Works steadily throughout the day, usually lasting over 24 hours without peaking.
Each type of insulin has its purpose, and many people use a combination to keep blood sugar levels stable throughout the day.
Step 2: Create a Routine with Your Healthcare Provider
Sit down with your doctor to design a routine based on your daily life. You’ll look at things like meal times, blood sugar patterns, and lifestyle needs. Most insulin regimens combine different insulin types to mimic how the body would normally release insulin.
Step 3: Regularly Check Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood sugar is key to knowing how well your insulin regimen is working. Aim to measure levels at regular times each day, especially before meals and at bedtime. This helps you and your doctor fine-tune your doses and spot any trends.
Step 4: Gather Your Insulin and Supplies
Before injecting, make sure you have everything ready:
- Supplies: You’ll need your insulin, syringes or insulin pens, alcohol swabs, and a sharps container.
- Inspect Your Insulin: Check for any cloudiness, crystals, or an expired date—if it doesn’t look right, don’t use it.
- Choose Your Injection Device:
- Syringe: For manually drawing and measuring insulin.
- Insulin Pen: A preloaded device that’s convenient and easy to use.
Step 5: Prep for the Injection
- Wash Your Hands: This keeps things clean and lowers the chance of infection.
- Pick Your Injection Site: Good spots are the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. Rotate between these areas to avoid hardening or irritation.
- Clean the Site: Use an alcohol swab and let it dry before injecting.
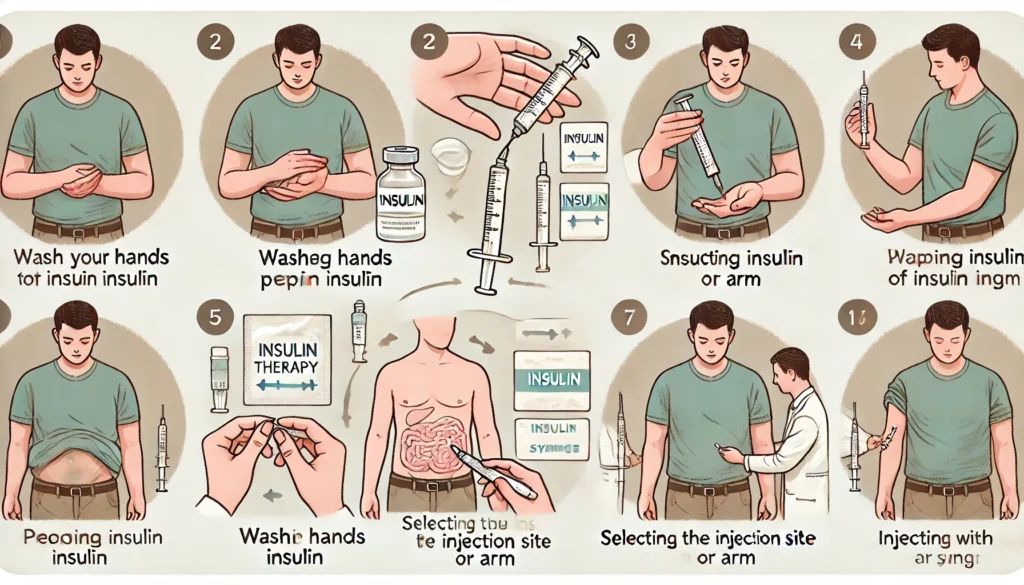
Step 6: Draw and Measure the Dose (For Syringe Users)
- Remove Any Air Bubbles: Insert the needle into the vial and draw up the insulin. Tap out any air bubbles.
- Measure Carefully: Use the markings on the syringe to ensure an accurate dose.
Step 7: Inject the Insulin
- Hold the Needle at a 90° Angle (or 45° if you’re injecting into a lean area).
- Insert the Needle Quickly to reduce discomfort.
- Inject Slowly: Press the plunger or button steadily to release the insulin.
- Hold for 10 Seconds: This helps prevent any insulin from leaking back out.
Step 8: Dispose of Used Needles Safely
Place used needles directly into a sharps container to avoid any accidents. Don’t recap the needle; just drop it in to keep things safe.
Step 9: Record Doses and Track Your Blood Sugar
Keep a log of your insulin doses, the time you took them, and your blood sugar readings. Over time, this helps you and your doctor adjust your regimen to fit your needs better.
Step 10: Monitor and Adjust Your Regimen as Needed
Regular check-ins with your doctor can help keep things on track. Adjustments are often necessary based on changes in activity levels, meals, stress, or overall health.
By following these steps and keeping in touch with your healthcare team, managing insulin can become a natural part of your routine. Being proactive and staying organized makes a big difference in managing diabetes successfully.
Here are some of the resources on insulin safety, dosage, and therapy:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA) – Insulin Basics
This ADA page covers the basics of insulin therapy, different types of insulin, and safe usage. https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/insulin-other-injectables/insulin-basics
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) – Insulin Safety
ISMP offers guidelines on safe insulin use, focusing on dosage accuracy and risk prevention.
https://www.ismp.org/recommendations/high-alert-medications-insulin
- Stanford Medicine (Diabetes Coalition of California) – Insulin Management
This guide provides tips for managing insulin in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, including starting doses and adjustments. https://med.stanford.edu/diabetes/mngt.html
- NHS (East London NHS Foundation Trust) – Insulin Therapy and Administration Guidelines
This NHS document includes guidance on insulin administration, self-administration protocols, and safety measures. https://www.elft.nhs.uk/resources/guidelines/insulin-therapy
People May Also Ask:
- What is the best time to take insulin?
The best time varies based on insulin type. Rapid-acting insulin is taken before meals, long-acting insulin is usually taken once daily at the same time each day.
- How do I know how much insulin to take?
Your doctor will help determine your dose based on blood sugar levels, meals, and physical activity. Blood sugar monitoring helps adjust doses over time.
- Where is the best place to inject insulin?
Common injection sites are the abdomen, thigh, and upper arm. Rotate sites to prevent skin thickening or scarring.
- How often should I check my blood sugar with insulin therapy?
Blood sugar should generally be checked before meals and at bedtime. Your doctor may recommend additional checks depending on your regimen.
- What should I do if I miss an insulin dose?
Consult your doctor or diabetes educator for specific guidance, as actions vary depending on the insulin type and time since the missed dose.
References:
- American Diabetes Association. (2022). Insulin basics. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/insulin-other-injectables/insulin-basics
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices. (2023). Safe practices for the use of insulin. Retrieved from https://www.ismp.org/recommendations/high-alert-medications-insulin
- Stanford Medicine. (2023). Diabetes Coalition of California: Insulin management. Retrieved from https://med.stanford.edu/diabetes/mngt.html
- East London NHS Foundation Trust. (2023). Guidelines on insulin therapy and administration. Retrieved from https://www.elft.nhs.uk/resources/guidelines/insulin-therapy