What is a vaccine?
A vaccine may be defined as live attenuated or inactivated modified whole or a part of microorganism which when administered into the body, does not cause disease whether it elicit a high humoral or cell mediated response and used as a prophylaxis against an infectious disease or against number of infectious diseases.

Types
- Live attenuated vaccine
- Inactivated/ killed vaccine
- Purified Macromolecules vaccine
- Recombinant Antigen Vaccine
- Recombinant vector Vaccine
- Synthetic peptide vaccine
- Multivalent Subunit Vaccine
- Anti-idiotypic vaccine
Live attenuated vaccine
- For live attenuated vaccine, whole microorganism is used and its attenuation is done. Attenuation is a process in which we serially grow or passage the microorganism such as bacteria or virus in an abnormal host or media until it loses its pathogenicity but it retains its immunogenicity. The example of an attenuated bacterial vaccine is BCG (Bacillus Calmattee Guerin) which is vaccine for tuberculosis mainly caused by a bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the example of attenuated viral vaccine is polio vaccine. Polio vaccine has two live attenuated strains i.e. Sabin and Salk.
- Advantages:
- High and quick immune response
- Prolong immunity
- No need of booster dose
- Disadvantages :
- It can revert back to virulency
- Storage and transport issues
- Post vaccination reactions
Inactivated/ killed vaccine
- For inactivated vaccine, microorganism is taken and its inactivation is done by physical or chemical methods. Inactivation means microorganism will not remain alive but its structure remains intact. To inactivation, different physical or chemical methods are used such as heat, formaldehyde, BEI (binary ethylenimine), β-propiolactone.
- Advantages:
- No safety issues
- No reversion back to virulency
- No issues of storage and transport
- Disadvantages:
- Low immunity
- Booster required
- Immunity for shorter duration
Purified macromolecules as vaccine
- In this, instead of using the whole microorganism, the part such as protein from microorganism is taken against which immunity is needed, then purified and then used as vaccine. These types of vaccines are also known as subunit vaccines. For example, for Hemophilus influenzae, its lipopolysaccharide capsule is taken, purified and then used as vaccine. The capsular LPS is used as vaccine against meningitis.
- Advantages:
- More specific.
- less un toward reactions.
- Disadvantages:
- Poor immunogenic.
- Difficulty in obtaining purified macromolecules in large quantity
Recombinant Antigen Vaccine
- Most immunogenic Antigen is cloned into an appropriate cloning vector, expressed in an expression host and used as vaccine after purification. The first ever recombinant antigen vaccine in animal was against Foot and mouth disease. While the first ever recombinant antigen vaccine in human was against hepatitis B virus.
- Advantages:
- Specific immune response.
- No reversion back to virulency.
- No un toward reaction.
- Minimum post-vaccination complications.
- Safe and stable.
- Disadvantages:
- Poor immunogen.
- Only humoral immune response not cell mediated.
Recombinant vector Vaccine
- For this recombinant vector vaccine, identify the gene segment in the genome of bacteria/virus which is encoding for the most immunogenic protein or peptide and then insert that gene segment into some biological vector (virus/bacteria which are non- pathogenic itself). Then it is inserted into the body as a vehicle which further attaches and enters into the cell and deliver gene to cell intracellularly. The classical example of recombinant vector vaccine Recombinant vaccinia that is the recombinant vector vaccine against small pox.
- Advantages:
- Specific immune response
- No post vaccination issues
- No storage and transport issues
- Disadvantages:
- Less immunogenic
Synthetic peptide vaccine
- For this the most immunogenic peptide is identified then the amino acid sequence of highly conserved region is identified which must have receptors on cell surface and capable of producing neutralizing Ab and used as vaccine. The first ever synthetic peptide vaccine was prepared against influenza. Nowadays scientists are working to prepare synthetic peptide vaccines against HIV, HBV, malaria and diphtheria.
- Advantages:
- No reversion back to virulency.
- No post vaccination stress.
- No stability and safety issues.
- Disadvantages:
- Less immunogenic.
Multivalent Subunit Vaccine
- There are many approaches for multivalent subunit vaccine but the common approaches are the use of ISCOMs and liposomes for these types of vaccines. In case of liposome one, the Ag is incorporated in to lipid vesicles using detergents and in case of ISCOMS, the Ag is incorporated into the protein miscles.
- Advantages:
- Better immunogenicity, both humoral and cell mediated.
- Immunity against number of diseases.
Anti-idiotypic vaccine
- An anti-idiotype vaccine is a vaccine made of antibodies which bind to other antibodies and stimulate the body to produce antibodies which attacks on tumor cells. These vaccines are a promising approach to cancer therapy because they have several advantages over conventional vaccines.
- Advantages:
- Safe and specific
Steps involve in Vaccine preparations
- Isolation, identification and characterization
- Purification and seed cultivation
- Attenuation or inactivation
- Quantification (CFU/ml, PFU/ml)
- Infectivity testing (LD50/ EID50/ TCID50)
- Adjuvants
- Tests (safety, stability, sterility, potency/ efficacy)
- Lyophilization
- Packing and labeling
- Marketing
Adjuvants
Adjuvants are not immunogen by themselves but tends to increase the immunogenicity. The examples of adjuvants which are mainly used are Alum, Freund’s incomplete & complete, Liposome and ISCOMs. They are used particularly when there is an issue of low immunogenicity.
COVID-19 vaccines
A covid-19 vaccine is a vaccine which aims to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the virus which causes coronavirus disease.
Some of the known and famous covid-19 vaccines are:
- Pfizer
- Moderna
- Novavax
- Sinovac
- Sinopharm
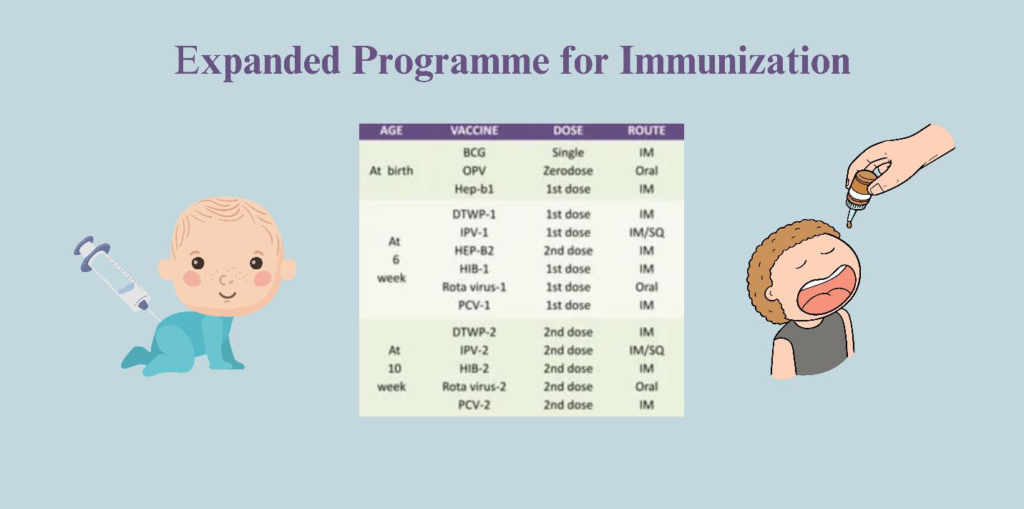
EPI program
EPI stands for Expanded Program on Immunization and it is a national immunization program which aims to reduce diseases and death due to infectious diseases caused by bacteria or viruses. In Pakistan, the EPI was established in 1978 to protect children aged 0-15 months and pregnant women against number of vaccine preventable diseases which includes childhood tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, hepatitis B, pneumonia, measles and influenza. According to EPI program, some of the vaccines are given once at birth while some required more doses with some specific gap after that. BCG is administered only once during birth and it do not require any booster dose or after dose. While other also administered according to their schedule.
The some of the goals of EPI program include:
- To reduce deaths and disabilities caused by diseases.
- To reduce infant mortality rate.
- To save lives.
- On the other hand, small pox is eradicated from the world as a result of vaccinations. Overall, it is concluded that diseases can be prevented by getting vaccinations.
FAQs
Who invented the small pox vaccine?
Dr Edward Jenner created the world’s first successful vaccine against smallpox and found that people infected with cowpox were immune to smallpox.
What is the difference between antibiotic and vaccine?
Antibiotics are taken as medicine when ill and vaccines are given before becoming ill as a prophylaxis.
Do vaccines provide natural immunity against disease?
No, vaccine provides artificially acquired active immunity against specific diseases.
Do vaccines cause autism as a side effect?
Some vaccines have many post vaccinations issues but they do not cause autism as a side effect.
Is natural immunity better than vaccine acquired immunity?
Active immunity which is acquired through vaccination is long-lasting while the length of natural immunity depends on the disease.