Key Words
Athlete’s foot, Tinea pedis, Foot infection, Fungal infection, Foot itching
INTRODUCTION
Athlete’s foot also known as Tinea pedis is a very common fungal infection that starts between the toes and might spread further to the soles. It is a contagious disease means you can acquire it by someone that has the disease or by walking on the floor barefoot containing the infectious organism. (Syc-20353841 @ Www.Mayoclinic.Org, n.d.)
CAUSATIVE AGENT
Athlete’s foot is caused by a dermatophyte fungus named T rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum. In all these fungi, T rubrum is the most common causative agent causing 70% of infection. (Tinea-Pedis @ Dermnetnz.Org, n.d.)
RISK FACTORS / ETIOLOGY
- All persons are not equally susceptible to fungal infection even they have similar risk factors. The factors that increase the risk of getting infection are underlying diseases such as Diabetes mellitus, lymphomas, older age, cushing’s syndrome.(Management_of_tinea_corporis,_tinea_cruris,_and @ Journals.Lww.Com, n.d.) Tinea pedis is usually occur in male/ adolescent but can also effect women. If you have the following conditions, you are at higher risk of getting infection.
- Sweaty foot
- Share shoes, socks and other footwear with someone having the same infection.
- Barefooted walk in public rooms such as locker rooms, swimming pools, steam rooms
- Wear enclosed or occlusive footwear such as heavy industrial boots
- Diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency
- Using medicines that suppress immune system (Syc-20353841 @ Www.Mayoclinic.Org, n.d.)

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Minor skin or nail injury, temperature, humidity or occlusion in toe cleft provide suitable condition to the infection to progress. Dermatophyte fungi contain an enzyme keratinase that invade the superficial keratin of skin that results in limitation of infection in this layer. Dermatophytes penetrates in host through Proteases enzymes that digest the keratin network into oligopeptides and amino acids and trigger immune response. (Management_of_tinea_corporis,_tinea_cruris,_and @ Journals.Lww.Com, n.d.) In response, the keratin cell secrets cytokines to fight dermatophytes. Moreover, dermatophyte cell wall contains molecules known as “mannans” that suppress the body immune response. (Fca05007996c45853f21a235b857416827ecb214 @ Www.Ncbi.Nlm.Nih.Gov, n.d.)
SYMPTOMS
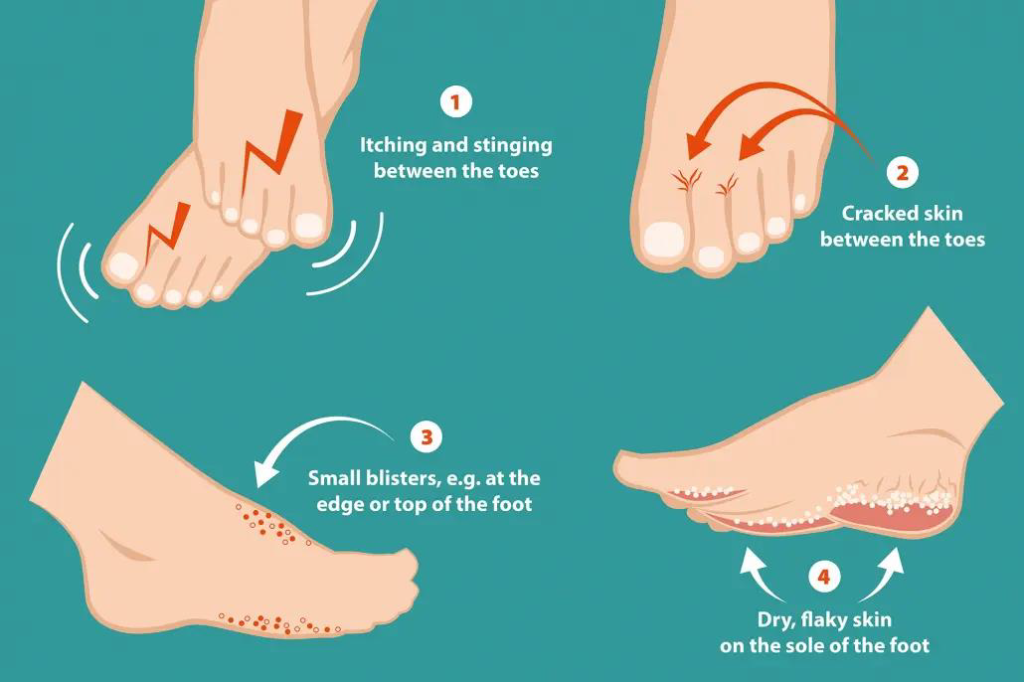
Some signs and symptoms of Athlete’s foot are as follows:
- Peeled or cracked skin between the toes
- Itching/ Itchy erosions
- Scales between the toes especially between 4th and 5th toe.
- Blisters
- Inflamed skin that appears reddish
- Discolored toe nails
- Raw skin under feet (Athlete’s-Foot @ Www.Healthline.Com, n.d.-a)
DIAGNOSIS
A doctor may diagnose the Athlete’s Foot by looking at the symptoms. This diagnosis includes physical examination of foot or investigating medical history of the patient and risk factors. If doctor is not sure about the fungal infection, a skin test is advised.
In this procedure, a sample from skin scraping can be obtained by No. 15 blade. The skin specimen is transported to presterilized black chart paper that keep the skin dry to avoid the growth of bacteria. (1091684-Workup @ Emedicine.Medscape.Com, n.d.)
Microscopic Examination
Skin specimen is then treated with 10-20% potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution. The KOH solution destroys normal cells and leaves the fungal cells untouched so that they can be easily seen under the
microscope. The infection is characterized by the presence of long, smooth, refractile, branched and septate hyphal filaments.
Cultural and antifungal sensitivity
SDA media (SDA, 4% peptone, agar, water, 1%glucose) is isolation media used for the diagnosis of fungal infection. Colony takes 7-14 days for development.
Dermatophyte test Media is another media that contains pH indicator phenol red. It takes 5-14 days to incubate at room temperature. The medium turns from yellow to bright red that shows the presence of dermatophytes.(Management_of_tinea_corporis,_tinea_cruris,_and @ Journals.Lww.Com, n.d.)
COMPLICATIONS
Athlete’s foot can lead to the other complications. It can spread to other warm and moist parts of the body. Allergic reaction to the fungus can lead to the blistering on hand and foot. If bacterial infection develops, Foot may be swollen, painful and hot. Pus and fever can be additional signs. (Athlete’s-Foot @ Www.Healthline.Com, n.d.-b)
Secondary cellulitis and lymphangitis can result from mycotic infections of the feet including tenia pedis. (1091684-Clinical @ Emedicine.Medscape.Com, n.d.)
TREATMENT
Topical and oral both antifungal therapies are used for the treatment of Tenia Pedis.
Topical Antifungal Therapy
Athlete’s Foot usually respond to Topical antifungal therapy. These includes allylamines, imidazoles, pyridones, benzylamines. Allylamines are considered more efficacious than azoles for the treatment of Athlete’s Foot. Topical antifungals are used for 1-6 weeks depending on manufacturer’s recommendations.
Some topical antifungals are:
- Imidazoles (Ketoconazole, Econazole, Clotrimazole 1%, miconazole, luliconazole)
- Pyridones (ciclopirox 1%)
- Allylamines (Terbinafine topical, Naftifine)
- Benzylamines (Butenafine)
Oral Antifungal Therapy
Oral therapy is indicated in case of patients that fail to respond the topical therapy. It should be considered in patients with extensive chronic hyperkeratotic or inflammatory tinea pedis. Oral therapy is generally given to 4-8 weeks.
Some oral antifungal medications are:
- Itraconazole
- Terbinafine
- Fluconazole (require long term treatment)
- Griseofulvin (require long term treatment) (1091684-Medication @ Emedicine.Medscape.Com, n.d.)
PREVENTION
There are several things that can be applied to prevent occurrence and reoccurrence of Tinea pedis such as:
- Try to let your feet air out as much as possible.
- Rinse and dry your feet thoroughly.
- Wash socks, bedding and towels at 60⁰C or higher.
- Apply a medicated foot powder once or twice daily.
- Use alternative pair of shoes.
- Don’t share shoes, socks or towels with others.
- Put antifungal powder on shoes.
- Chlorine bleach is a disinfectant that kills mold and can be used to clean bathroom floors. (Syc-20353841 @ Www.Mayoclinic.Org, n.d.)

CONCLUSION
A fungal infection commonly affecting the skin in between the toes, athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is contagious and typically affects people who have sweaty feet and are restricted to tight shoes. Dermatophyte fungi, such as Trichophyton rubrum, T. interdigitale, and Epidermophyton floccosum, are the cause of it. Common signs and symptoms include redness, blisters, burning, and scaly, cracked skin. The infection is more likely in people who regularly wear enclosed footwear, go barefoot in public places, or exchange personal belongings with infected people. It is spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as floors, towels, or shoes. Though mostly clinical, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) skin test may be used to make the diagnosis. Oral or topical antifungal medication is part of the treatment. Preventive actions include changing socks frequently, keeping feet dry, and
PEOPLE ALSO ASK FOR
What is the main cause of tinea pedis?
The main cause of tinea pedis is sweaty foot mainly confined in tight shoes. The other causes includes exposure directly to the causative agent.
What is the best treatment for tinea pedis?
The treatment of tenia pedis includes application of topical antifungal. Moreover, keep your feet dry and clean and don’t share shoes, socks and towels with others.
What are main 3 symptoms of athlete’s foot?
Main symptoms of tenia pedis are itchy erosions between your toes, reddish skin and scales on the skin.
How I can treat Athlete’s foot at home?
At home, Vinegar Foot Soak can be used to slow down foot fungus. Vinegar has antifungal and antibacterial properties that slow the growth of foot fungus and also prevent skin infections.
What is the rule of 2 in tinea?
For at least two weeks following clinical remission, the topical antifungals should be administered two centimeters beyond the lesion’s edge.






