WHAT IS DIARRHEA?
Diarrhea is a common condition usually characterized by frequent watery or loose bowel movements. It can be acute or chronic, and its impact on daily life can be significant. Whether it’s caused by a viral or bacterial infection, food intolerance, or an underlying medical condition, diarrhea can leave you feeling drained, dehydrated, and uncomfortable. Either it is a symptom of a major disease or a result of a common body infection.
SYMPTOMS
- Loose watery stool: urgent need to defecate
- Sharp Abdominal pain and bloating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dehydration: includes too much electrolyte and fluid loss, dry mouth, decreased urination, and dizziness.
- Fever and chills: usually occur in viral and bacterial infections.
- Blood and mucus in stools: It signals a serious underlying medical issue.
CAUSES
- Bacterial and viral infections: include gastroenteritis, commonly known as a stomach bug.
- Food poisoning and traveler’s diarrhea
- Medications: antacids with Magnesium, antibiotics, overuse of laxatives, and cancer drugs.
- Food intolerance: lactose intolerance and celiac disease.
- Bowel affecting disease: IBS (inflammatory bowel syndrome), ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease.
- Surgery and other procedures.
TYPES
- Acute diarrhea: acute loose movement of bowel for 1to 2 days and resolves on its own.
- Persistent diarrhea: loose stools that last for 2 to 4 weeks as a result of some infection.
- Chronic diarrhea: lasts more than 4 weeks and goes on for a long period.
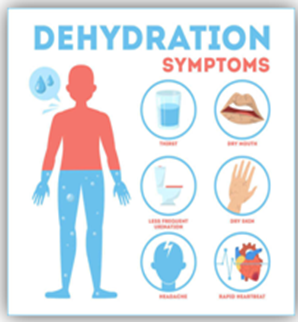
COMPLICATIONS OF DIARRHEA: DEHYDRATION
It is the major complication that the patient faced, as it affects the bodily functions.
- Without treatment, it can lead to kidney failure, stroke, heart attack, and even death.
- Headache, flushed dry skin, severe nausea, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue.
- Dark urine color.
- Less than 6 wet diapers in a day for children signals a serious effect of diarrhea on the human body.
DIAGNOSIS OF DIARRHEA
- BLOOD TEST: Kidney function test, CBC, or electrolyte measurement tests can be done to rule out fluid loss.
- STOOL TEST: to rule out bacteria or parasites causing infection, e.g., ROTAVIRUS test.
- HYFROGEN BREATH TEST: to determine lactose intolerance, a liquid with a high level of lactose is consumed, and your breath is measured for hydrogen at regular intervals.
- COLONOSCOPY OR UPPER ENDOSCOPY.
TREATMENT OPTIONS:
- AT HOME TREATMENT AND REMEDIES:
- Rehydration:
Drink plenty of fluids to replace fluid and electrolyte loss.
Water, clear broths, and oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are the best possible options.
- BRAT diet:
Bland foods like mashed rice, soft toast, blanched apple puree, banana, curd, semi-solid, and low fiber diet.
- Zinc supplements:
They reduce the frequency and volume of stools, especially in children.
- Over-the-counter medicines (OTC):
Bismuth subsalicylate or loperamide can help to control the symptoms in adults only.
- Avoid greasy and fried foods.
CAUTION:
Without any proper diagnosis from a doctor, don’t use METRONIDAZOLE (flagyl) as an OTC, as it’s only indicated if you have 10 loose stools in a day.
Some people force-feed the patient during diarrhea, which may cause vomiting and nausea, making the situation worse.
- MEDICAL TREATMENT:
A health care provider, after carefully examining the cause of the disease, will recommend a medicine.
- ANTIBIOTICS AND ANTHELMINTHICS:
Diseases like Rotavirus or any bacterial infections, or parasitic infections usually require a 5 to 7-day course.
Azithromycin is usually prescribed for acute diarrhea and dysentery.
- ANTICHOLINERGICS: include dicyclomine to treat spasms due to painful bowel movement.
- BILE ACID BINDERS:
Prescription medicine related to Irritable bowel syndrome requires bile acid binders.
- Intravenous FLUIDS:
Required when constant vomiting is there and has resulted in severe dehydration.
- PROBIOTICS:
To introduce beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- FOODS TO AVOID:
- Spicy foods
- Fried or fatty foods
- Milk and dairy (except if it contains probiotics)
- Citrus fruits
- Foods that are high in sugar
- Coffee and other drinks with caffeine
- Vegetables that can give you gas, such as beans, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts
CONCLUSION
Diarrhea is a common condition characterized by frequent, watery, or loose bowel movements, often caused by infections, food intolerance, or underlying medical conditions. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, dehydration, and fever. Treatment involves rehydration, dietary changes, and medication, while complications can lead to dehydration, kidney failure, and even death if left untreated. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What causes diarrhea?
Diarrhea can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, food intolerance, medications and underlying medical conditions.
When should I seek medical attention for diarrhea?
You should seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like blood in stool or if diarrhea persists for more than 3 days.
Can diarrhea lead to dehydration?
Yes, diarrhea can lead to dehydration, especially if not treated promptly.