Introduction
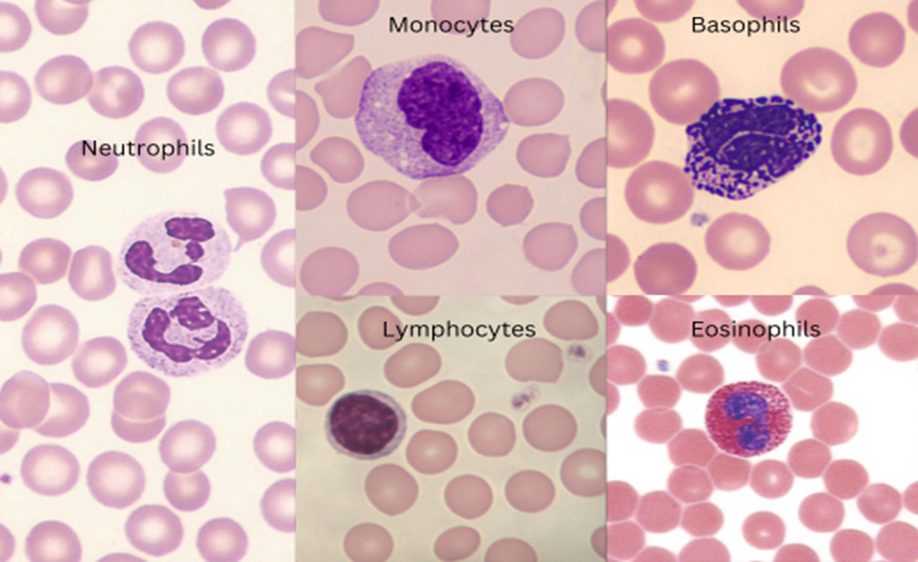
The immune system protects our body from outside invaders and immune cells are a part of the body immune system which help to fight infections and diseases in body. They basically originate from stem cells in the bone marrow during the process of hematopoiesis and further develop into different types of cells known as white blood cells (WBCs). Some of the types of immune cells include:
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Dendritic cells
On the basis of the presence or absence of cytoplasmic granules, the White blood cells are categorized into two main categories i.e. Granulocytes and Agranulocytes. Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils are known as granulocytes because they have cytoplasmic granules in them while lymphocytes, monocytes and dendritic cells are known as Agranulocytes because they do not have cytoplasmic granules.
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are the central and major cells of the immune system and they contribute about 25% of the total White blood cells and they are 99% of the cells in the lymph and if we weight these then it is 1012 which is equivalent to the combine weight of brain and liver. So, the number of lymphocytes in a healthy immunocompetent individual is 1012. They are the major cells because they have four properties or functions which include:
- Specificity
- Memory
- Diversity
- Self or non-self recognition
On the basis of their receptors, there are further three types of lymphocytes which include:
- B lymphocytes or B-cells
- T lymphocytes or T-cells
- Null cells
They all are morphologically similar, motile and are all non- phagocytic. But they have different surface receptors on them, on the basis on these receptors, they can be distinguished.
B-cells/ B-lymphocytes:
They are named as B-cells because their site of formation and maturation is Bone Marrow in case of mammals and in case of birds, their site of maturation is Bursa of Fabricius.
T-cells/ T-lymphocytes:
They are named as T-cells because their site of maturation is Thymus but they formed in bone marrow as B-cells forms during the process of hematopoiesis.
Null cells:
Null cells are those which have neither T-cell receptors nor B-cell receptors on them that’s why they are named as null cells. One of the functional cells of null cells are Natural killer cells. They are anti-cancerous means they help to kill cancerous or tumorous cells. They kill tumor in two ways:
- First one is either through direct contact through antibody independent process.
- Second one is the specific antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity.
Monocytes
Monocytes are mononuclear cells because they have single nucleus. They are called as monocytes when they are present in the circulation (blood). But when monocytes go into tissue from blood then they are called macrophages which means there are certain changes take place when a blood monocyte enter into tissue spaces. Some of the changes which take place are:
- It increases in size (increases 5-10 folds).
- It increases in number and complexities of their cellular organelles.
- It starts secreting more lytic enzymes and soluble factors.
- Cell acquires more phagocytic activity.
The main function of the macrophages are that they involve in the process of phagocytosis.
Neutrophils
They are polymorphonuclear cells means their nucleus is multi-lobed. Their cytoplasmic granules are neutral because they can be stained by both acidic and basic dye. Their phagocytic activity is more than macrophages.
- Their function is that Neutrophils are the 1st line of defense against infection and they are the 1st cells to reach at the site of inflammation.
- The increase in White blood cells particularly the neutrophils, this condition is known as leukocytosis and it indicates an acute infection.
Eosinophils
They are bilobed and are granulated. Their cytoplasmic granules are stained with the acidic dye that is Eosin. They are phagocytic but their phagocytic activity is less than neutrophils and macrophages. The cytoplasmic granules of Eosinophils secrete some anti- parasitic substances which causes damage to the parasite’s cell membrane and further kills parasites.
- They play very important role in immunity against parasites.
Basophils
They have single lobed nucleus. When they are in blood then called as basophils but when they migrate or go into tissue then they are called as Mast cells. Basophils are stained with basic dye that is methylene blue. Mast cells secrete many active substances, one of them is Histamine. Histamine plays an important role in allergy and allergic reactions.
Dendritic cells
Dendritic cells are also the immune cells like other immune cells. Their cytoplasmic process on them, they are similar to that of dendrites present on neurons. They synthesize major histocompatibility complex (MHC-II) so act as APCs which are antigen processing cells. So, the dendritic cells are the most common and powerful APCs. They can be of two types which include:
- Lymphoid dendritic cells
- Non- lymphoid dendritic cells
Lymphoid dendritic cells are those dendritic cells which are present in lymphoid or Immune organs. They further are of two types:
- Interdigitating lymphoid cells:
They are present in T-cell rich area such as spleen, lymph node and thymus and they act as APCs as they present the antigen to T- helper cells.
- Follicular lymphoid cells:
They are present in the lymphoid follicles of lymph nodes and they present the antigen to B-cells and they help to activate B-cells.
FAQs
- During the interpretation of CBC report, if increase in number of neutrophils is observed then what it indicates?
It indicates an acute infection in the body.
2. Eosinophilia indicates what and which immune cell act against parasitic infection?
Eosinophilia indicates a parasitic infection and eosinophils are the cells which are anti- parasitic.
3. As all lymphocytes (B-cells, T-cells and Null cells) are morphologically similar then how to distinguish them?
They can be distinguished on the basis of their surface receptors.
4. Do platelets and red blood cells have role in immunity?
RBCs and platelets have nothing to do in immunity so they have no role in immune system.
5. Which immune cells are known as anti- cancerous cells?
Natural killer (NK) cells are anti- cancerous cells.





