Prebiotics and probiotics are generally considered as two distinct concepts that work together to support gut health
What are Probiotics?
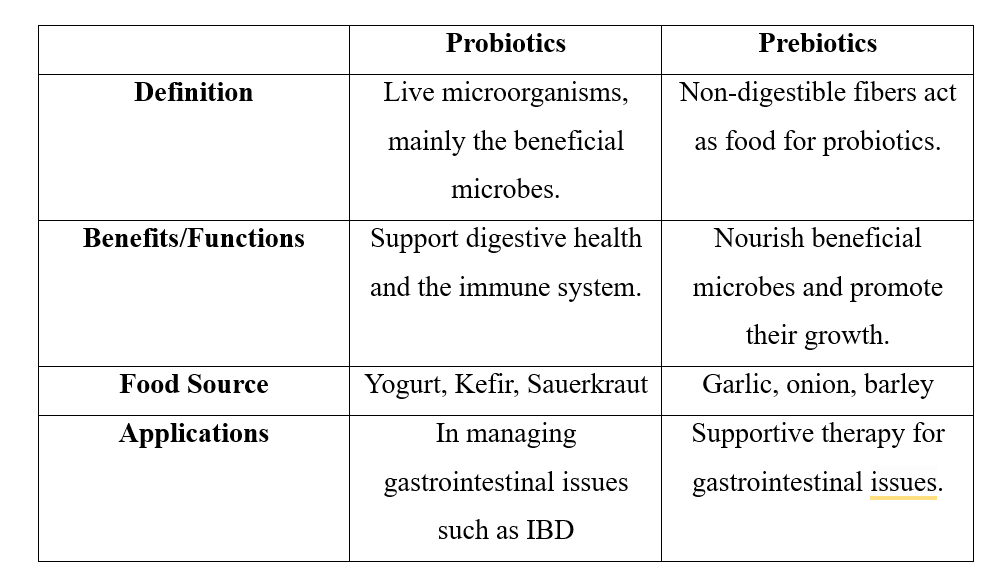
Probiotics are mainly live microorganisms, particularly known as beneficial bacteria (good bacteria). They mainly support digestive health, such as in managing irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, and diarrhea. They also support the immune system by boosting the body to fight infections. They can also improve skin health, such as acne and eczema etc.
What are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial bacteria known as probiotics. They particularly nourish beneficial bacteria in the gut and
further allow them to grow, and also increase the absorption of minerals, ultimately maintaining a healthy balance in the gut microbiome.
Probiotic-rich foods mainly include yogurt, kefir, and kombucha. Prebiotic-rich foods mainly include onion, garlic, etc
Common Probiotic Bacteria
• Lactobacillus strains, particularly Lactobacillus acidophilus, support digestive health.
• Bifidobacterium bifidum also supports gut and immune health.
• Streptococcus thermophilus is commonly used in combination with Lactobacillus to support the overall health of the gut.
• Bacillus coagulans also supports gut health.

Antibiotic Resistance and Probiotics
Probiotics play an important role in various ways, including,
• By restoring Gut Microbiota ultimately maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which may be disrupted by antibiotics.
• By supporting the immune system, they can help in preventing infections, which ultimately reduces the need for antibiotics.
Overall, some probiotics can inhibit the growth of pathogens, particularly the antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and some probiotics improve gut and immune system health, which further improves overall health.
UNDERSTANDING THE DIFFERENCE
CONCLUSION
Overall, Probiotics and prebiotics play an important role in supporting gut health and boosting the immune system. Probiotics are mainly beneficial bacteria, and prebiotics act as food and nourish probiotics, ultimately promoting a balanced gut microbiome. Some of the common probiotics, including Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Streptococcus thermophilus, and Bacillus coagulans, promote gut health.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQS)
- Are there any side effects of Probiotics?
Answer: There are no serious side effects, but some may experience temporary bloating, diarrhea. - Can we eat prebiotic and probiotic foods at the same time?
Answer: Yes, it’s best to take both foods together to get proper benefits. - Can the antibiotic issue be overcome by the use of probiotics?
Answer: By supporting the immune system and gut health, probiotics can help in preventing infections, which ultimately reduces the need for antibiotics.
REFERENCES
Toqeer SR, Jameel N, Sajid M, Ikram L, Abbas T, Khalid M, Dilawar A, Tanveer F, Bukhari SS and Nadeem H, 2025. Gut microbiota and weight regulation: the role of probiotic and prebiotic interventions. In: Aadil RM, Salman M, Mehmood K and Saeed Z (eds), Holistic Health: Gut Microbiota and Holistic Health: The Role of Prebiotics and Probiotics. Unique Scientific Publishers, Faisalabad, Pakistan, pp: 110-118. - Sanders, M.E., Merenstein, D.J., Reid, G., Gibson, G.R. and Rastall, R.A., 2019. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology, 16(10), pp.605-616.







