The Thyroid gland is a small gland located in the neck, and it plays an important role in regulating the body’s metabolism. Moreover, it is a part of the endocrine system and produces thyroid hormones, including T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which control and regulate various body functions. In contrast, when the thyroid does not work properly and does not produce the right amount of hormones, it is commonly known as thyroid disease, which can affect people of all ages, but some studies show a higher prevalence in females and with increasing age.
TYPES OF THYROID DISEASE
There are two main types of thyroid disease, and there are many factors and conditions that can cause them.
•Hypothyroidism (Underactive thyroid)
•Hyperthyroidism (Overactive thyroid)
CONDITIONS THAT CAUSE HYPOTHYROIDISM
•Iodine deficiency
•Autoimmune condition
•Congenital hypothyroidism
CONDITIONS THAT CAUSE HYPERTHYROIDISM
•Excessive Iodine
•Autoimmune condition
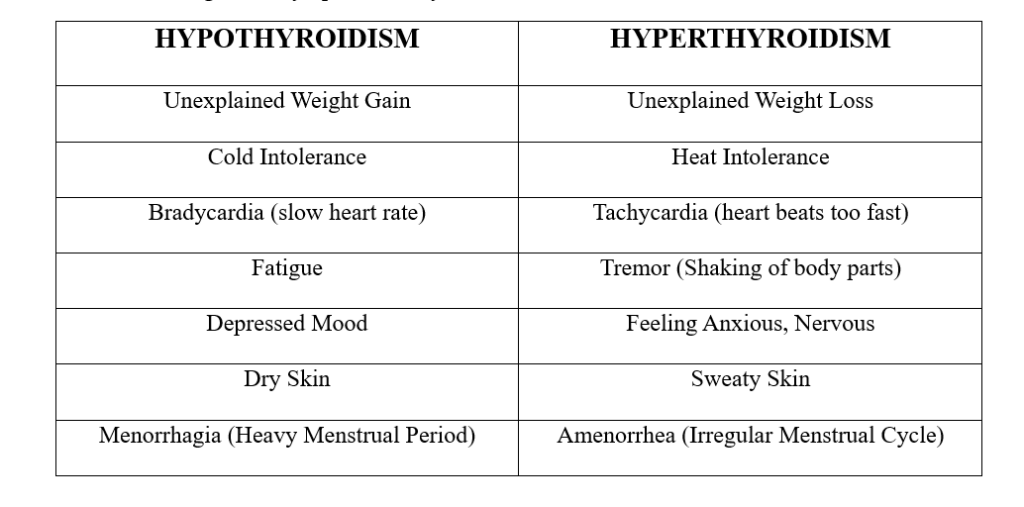
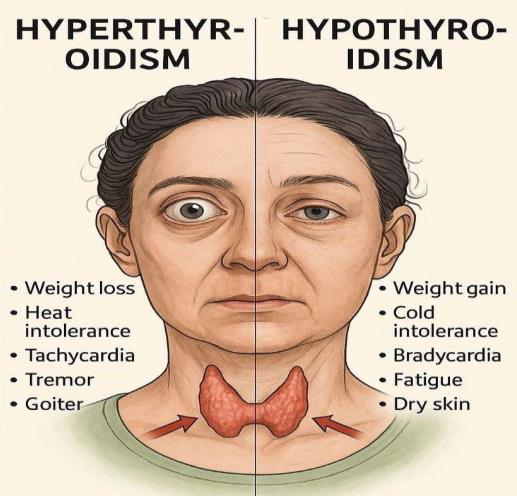
SYMPTOMS
The common signs and symptoms of thyroid diseases are as follows:
DIAGNOSIS
There are various methods to diagnose thyroid disease, which include the following:
•Symptoms and Medical history
•Physical Exam
•Blood Test: The Thyroid blood tests include T3, T4, TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone), and thyroid antibodies.
•Imaging Test: Imaging tests, like a thyroid ultrasound to check nodules (lumps) or goiter.
TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT
Treatment for thyroid disease depends on the type of the disease. However, the ultimate goal is to manage and regulate the levels of the thyroid hormones to a healthy level.
For the management and treatment of hypothyroidism, the main treatment option is thyroid replacement medication, by again providing hormones to the body in a synthetic way. The most common medication that is mainly prescribed in case of hypothyroidism is Levothyroxine.
In contrast, for the management and treatment of hyperthyroidism, antithyroid drugs commonly used are methimazole and propylthiouracil. In addition, some medications do not directly treat hyperthyroidism but help to manage some associated symptoms, such as beta-blockers to manage rapid heart rate. Moreover, Radioiodine/radioactive therapy can also be done in many cases. In addition, a surgical treatment commonly known as thyroidectomy can be done in severe cases, and as a permanent treatment for hyperthyroidism.
FOODS TO INCLUDE FOR THYROID HEALTH
•Leafy green vegetables
•Fruits
•Whole grain
•Lean Protein
FOODS TO AVOID FOR THYROID HEALTH
•Processed food
•Gluten diet
CONCLUSION
Thyroid disease mainly affects the thyroid gland and ultimately affects the production of thyroid hormones and leading to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Their symptoms depend on the type of disease. Overall, understanding thyroid disease is important in managing and treating the disease.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (FAQS)
HOW TO PREVENT THYROID PROBLEMS?
Thyroid problems associated with genetics and autoimmune conditions cannot be prevented, but ensuring sufficient iodine intake can help prevent thyroid problems.
WHAT ARE THYROID NODULES?
These are mainly the lumps on the thyroid glands and can be benign or cancerous.
HOW TO MANAGE THYROID DISEASE?
With proper care, treatment, following precautionary measures, and regular monitoring, thyroid disease can be managed.
REFERENCES
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8541-thyroid-disease
https://medlineplus.gov/thyroiddiseases.html







