Etiology
The main causative agent of typhoid fever is Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi, both are members of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- Salmonella is a genus that has two species Salmonella enterica serovar and enteritidis.
- Both Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi (A, B, C) are Salmonella enterica serotype.
Risk Factor
Salmonella is transmitted by the fecal-oral route through contaminated water, undercooked foods, fomites of infected patients, and is more common in areas with overcrowding, social chaos, and poor sanitation.
Symptoms
The symptoms of typhoid fever usually develop 1 or 2 weeks after a person becomes infected with the Salmonella typhi bacteria.
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Abdominal pain with diarrhoea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Enlarged liver
- Skin rashes
- Hallucinations
- Delirium
Diagnostic test of Typhoid
There are some common tests for diagnostic of Typhoid fever.
Blood test
- For the culture, a small sample of your blood, stool, urine or bone marrow is placed on a special medium that encourages the growth of bacteria.
- The culture is checked under a microscope for the presence of typhoid bacteria. A bone marrow culture often is the most sensitive test for Salmonella typhi.
The Widal Test
- The Widal test measures the capacity of antibodies against LPS OR flagella in the serum of individuals with suspected typhoid fever to agglutinate cells of S. Typhi; the test was introduced over a century ago and it is still widely used.
- It is simple, inexpensive, and takes only a few minutes.
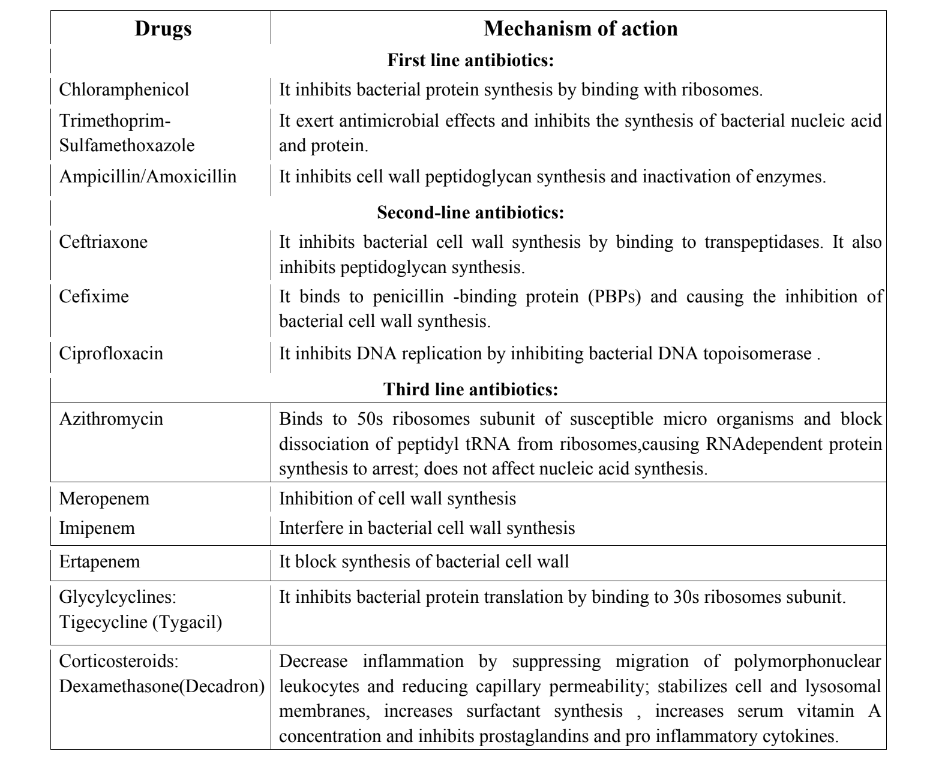
Standard Treatment
If typhoid fever is diagnosed in its early stages, a course of antibiotic tablets is prescribed. Most people need to take these for 7 to 14 days. Following are the drugs prescribes to treat typhoid fever.
Vaccination for Typhoid Fever
Inactivated typhoid vaccine is administered as an injection (shot). It may be given to people 2 years and older. Repeated doses are recommended every 2 years for people who remain at risk.
Counseling plan
Your symptoms should begin to improve within 2 to 3 days of taking antibiotics. But it’s very important you finish the course to ensure the bacteria are completely removed from your body. Make sure you rest, drink plenty of fluids, and eat regular meals.





