INTRODUCTION
Heart is the vital organ of the body, tirelessly pumping blood and providing oxygen and nutrients to each and every cell of the body. So heart health is the cornerstone of the circulatory system.
Understanding heart health is not only crucial for medical student but for general public also. This article evaluates the basic concept of heart and its component and provides the basic knowledge to maintain a healthy life.
BASIC FUNCTION OF THE HEART
Human heart is a muscular organ roughly having the size of a fist and located slightly to the left of chest’s midline. It contains 4 basic chambers
- 2 atria (upper chamber)
- 2 ventricles (lower chamber)
The heart operates through repetitive cycle of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) and this cycle is regulated by electric impulses origination from SA (sinoatrial) node. As a result heart has a coordinated and rhythmic heartbeat.
COMMON HEART DISEASES
Any problem in the heart or its component leads to heart disease and heart diseases are collectively referred to as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). CVDs are the leading cause of death worldwide.
Common heart diseases are as follows
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup.
- Heart Failure: Inability of the heart to pump blood efficiently.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats caused by electrical signal disruptions.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Chronic elevation in blood pressure
- Valvular Heart Diseases: Malfunctions in heart valves affecting blood flow and heart functions
SYMPTOMS OF HEART PROBLEMS
Some heart conditions remain silent, common warning signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina).
- Shortness of breath.
- Fatigue or dizziness.
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats.
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet (edema).
RISK FACTORS FOR HEART DISEASE
Many factors increase the risk of developing heart diseases:
- Non-Modifiable Factors:
- i) Age (risk increases with age).
- ii) Gender (men are at higher risk earlier in life).
- iii) Family history of heart disease.
b) Modifiable Factors:
- Poor diet (high in saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium).
- Sedentary lifestyle (low energy and motivation)
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Stress and poor sleep.
- Uncontrolled diabetes and high cholesterol levels.
PREVENTION OF HEART DISEASE
Prevention is better than cure, and maintaining heart health involves a healthy approach:
- Healthy Diet
- a) Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- b) Reduce intake of saturated fats, sugar, and salt.
2) Regular Exercise
- a) Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- b) Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling improve cardiovascular fitness.
3) Avoid Smoking
- a) Smoking damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
4) Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
- a) Monitor levels regularly and follow medical advice.
5) Manage Stress
- a) Practice mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS
Early detection of heart issues significantly improves outcomes. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects electrical activity irregularities.
- Echocardiogram: Provides images of heart structures.
- Stress Tests: Assess heart function during physical exertion.
- Blood Tests: Measure cholesterol and markers of heart damage.
- Angiography: Visualizes blockages in coronary arteries.
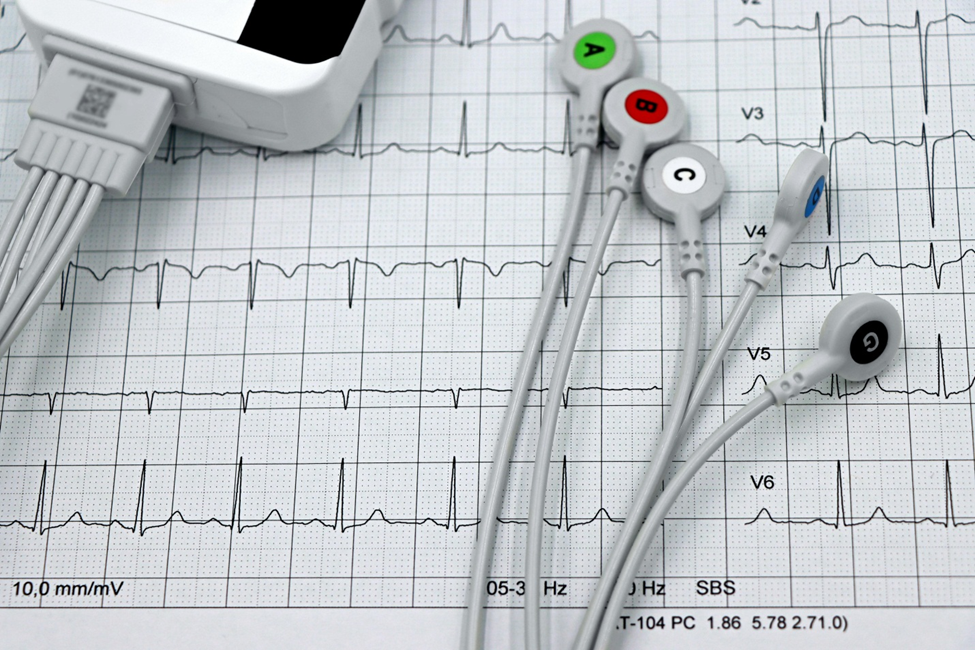
Early issue detection of a heart disease can saves a person from painful and expensive treatment. Depending upon the heart health following approaches can be used
- Lifestyle Changes: First-line management for most conditions.
- Medications: To control blood pressure, cholesterol, or prevent clots.
- Surgical Interventions: Angioplasty, stent placement, or bypass surgery.
HEART HEALTH AWARNESS
It is very important for people to have a basic knowledge about the heart health. Now days it is quite easy to have the basic information about the health and healthy lifestyle. A healthy heart can save you from a lot of medical complications.
CONCLUSION
Heart health is now a universal concern, demanding attention from medical professionals and the public also. By adopting preventive measures and understanding the basics of heart function and diseases, we can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Medical professional, as healthcare providers, hold the responsibility of spreading awareness and contributing to a healthier society.
FAQs
- What are the early signs of heart problems? Early signs include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and swelling in the legs or feet. Regular check-ups are essential to catch issues early.
- How can I reduce my risk of heart disease? Adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle by eating nutritious foods, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, managing stress, and controlling conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
- Is heart disease hereditary? Yes, a family history of heart disease can increase your risk. However, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce this risk.
- How often should I check my blood pressure and cholesterol levels? Adults should check their blood pressure at least once a year and cholesterol levels every 4-6 years, or more frequently if advised by a doctor.
- Can stress really affect heart health? Yes, chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and other risk factors for heart disease. Managing stress is an essential component of heart health.






