What is a Urinary tract infection?
urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection which can affect any part of the urinary system. Some infections affect the lower urinary tract which involves the bladder or urethra while some of the infections affect the upper urinary tract which mainly involves one kidney or both kidneys.
However, the healthy urinary system is composed of following four parts and mainly performs these following functions:
- Kidneys: Kidneys mainly filters blood and removes waste and water to produce urine.
- Ureters: These are two tubes which help to urine from kidney to the bladder.
- Bladder: It temporarily stores the urine.
- Urethra: It is a tube which allows the urine to exit the body.

Causes/Common micro-organisms involved in U TIs?
Urinary tract infections are mainly caused by variety of bacteria and even fungi or yeast also causes UTIs. The bacteria including gram- positive or gram- negative and fungi mostly enters the urinary tract and start multiplying there and as a result causes UTIs. The most common pathogen which causes UTIs is Escherichia coli, in almost 70-90 percent cases of UTIs, E. coli is isolated which is also present as normal flora in human colon. Hence, E. coli is considered as the main culprit in UTI. The other bacteria which cause UTIs are mainly:
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Staphylococcus aureus
While Candida albicans is the most common cause of fungal UTIs among patients.
Who is more at risk?
The women are more at risk of getting UTIs as their urethra is shorter and close to the anus and vagina than the men. However, due to this anatomy of the urethra in females, the bacteria from the anus easily enter the female urinary tract and further causes an infection known as urinary tract infection. On the other hand, older people and children are more at risk due to their weaker immune systems than young ones.
Risk factors associated with UTIs:
The risk factors which mainly associated UTIs are:
- A weak immune system.
- Insertion of urinary catheter.
- A past history of surgical procedures.
- A past history of taking some medications particularly antibiotics.
- Female gender.
- Older age group.
- Pregnant women.
Catheter associated UTIs:
A catheter associated UTI is a urinary tract infection caused by micro- organisms which enters the urinary system after inserting the urinary catheters and these infections are also considered as Hospital acquired infections (HAIs) because they are mostly acquired by hospital environment among patients admitting in the hospitals. There are many factors which are involved in catheter associated UTIs which involves:
- Prolonged use of urinary catheters.
- Contamination due bacteria present in stool.
- Not emptying the urinary bags.
- Improper cleaning of catheters etc.
UTI in pregnant women:
The risk of urinary tract infections are common in pregnant women due to such anatomical and physiological changes in the female body during pregnancy. This gestational UTIs should be treated in time as they can have serious affects on both mother and fetus. The hormonal changes during pregnancy are the main reason of UTIs in pregnant women.
Symptoms of UTI:
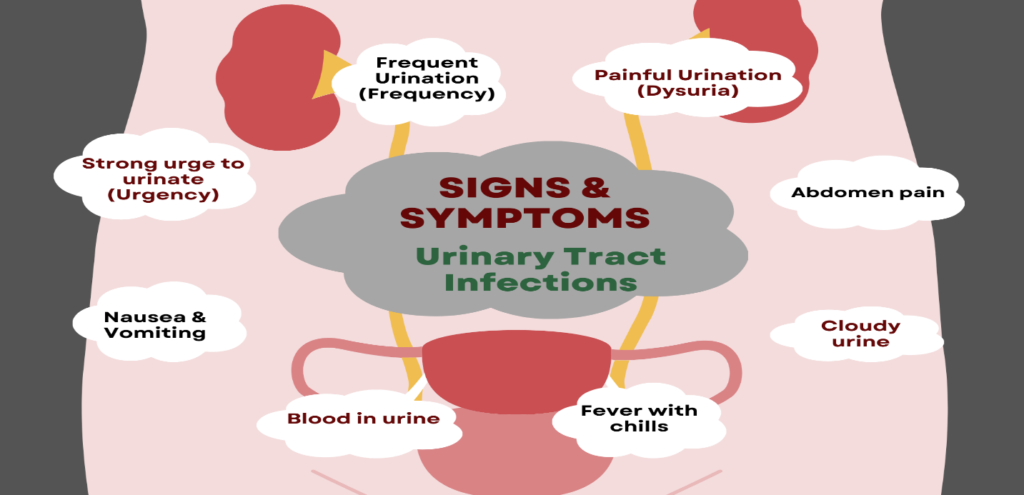
UTIs can be asymptomatic and can be symptomatic, the some of the common symptoms which are mainly observe in UTI patients are as follow:
- Dysuria which means painful urination.
- Frequent urination particularly at night.
- Strong urge to urinate.
- Cloudy or bloody urine.
- Urine with a bad odor.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Fever with chills.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Tiredness or feeling unwell.
Diagnosis:
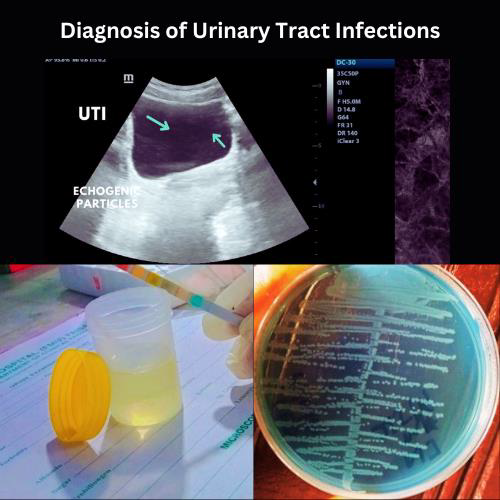
The UTI is mainly diagnosed on the basis of these following diagnostic techniques which involves:
- Urine dipstick
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture
- Ultrasound
Urine dipstick:
This is one of the fast ways to diagnose whether it is UTI or not. For this urine sample is collected in a urine container and sent to the laboratory. To perform this, a laboratory technician dips a urine strip containing chemicals on it, into the urine container. The chemicals on the strip change its color if there are white blood cells or bacteria present in the urine.
Urinalysis:
In this, urine sample is observed under the microscope to check any signs related to UTI. The white blood cells, blood or bacteria are observed under the microscope, if they are seen in microscopy then it indicates the UTI. This test can be performed if the urine dipstick test show negative results but patient has symptoms of UTI.
Urine culture:
For this test, clean catch and midstream urine is collected in a sterile container and sent to the laboratory for analysis. The laboratory technician typically processed the urine sample for culture and sensitivity. This usually takes 1to 2 days to check the growth of bacteria. This test is
reliable than other above one because it gives the report of bacteria isolated and also antibiotics susceptibility report. As in antibiotics susceptibility testing, different antibiotics are tested against bacteria isolated from urine, thus proper medications or antibiotics can be prescribe to the patient for proper recovery.
Ultrasonography:
Ultrasound is an imaging technique which can evaluate the condition of the kidneys and bladder and can help to diagnose UTIs.
Treatments:
Antibiotics are the only medications which can treat UTIs if taken according to proper prescription. Antibiotics treat UTIs by killing the bacteria or by stoping the growth of bacteria which cause the infections. The antibiotics for UTIs are not mainly available as Over the counter medications as they required proper prescription. Some of the UTIs can be treated with a short course of antibiotics, typically 1 to 3 days but pregnant women and patients with serious symptoms may need a longer course of antibiotics for proper recovery. Although, for proper treatment antibiotics should be taken after the results of the culture and sensitivity of urine. Some of the antibiotics which are prescribed for UTIs are:
- Timethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (combination of two antibiotics)
- Nitrofurantoin
- Fosfomycin
- Amoxicilin/clauvanic acid
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Doxycycline
Additionally, cranberry juice is also recommended to the UTI patients as it has some antibacterial properties as it flushes out bacteria from urinary system. But it is not used alone for treatment of UTIs, it is used along with antibiotics. While some painkillers are also prescribed along with antibiotics to get relieve from UTI related pain.
Antibiotic Resistance in UTIs:
Due to misuse and over use of antibiotics among patients, antibiotic resistance is become a major concern. Due to antibiotic resistance, mainly Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin (fluoroquinolones) along with other antibiotics are not effective against pathogens involve in UTIs. Thus, Nitrofurantoin and Fosfomycin are more effective in case of infections related to urinary system.
Preventions:
There are some precautionary measures which we can follow to avoid or reduce the urine infections such as:
- Consume enough water on daily basis to flush out toxins.
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
- Empty the urinary bladder before and after intercourse.
- Avoid strong soaps to clean genitals.
- Ensure proper hygiene practices by clean genitals properly and taking bath.
- Wear breathable undergarments and trousers.
- Increase uptake of vitamin C to boost immunity.
Conclusion:
Urinary tract infections are the infections in any part of the urinary system and are very common among women because of their anatomy. However, E. coli is the main culprit of UTIs and travels to the urinary system while passing stool as it is mainly present in the colon of human as normal flora. These infections are common among pregnant women and in patients in which urinary catheters are inserted along with other risk factors associated. Overall, these infections are treated with antibiotics after proper diagnosis and cause of UTI and it can be prevented by following different precautionary measures.
FAQs
How long do urinary tract infections last?
It depends on infection gets treated or not. If treated properly, symptoms subside within 48 hours of treatment.
Is cranberry juice effective for UTIs?
They are not used as treatment alone instead they are used to prevent from happening.
Are UTIs contagious?
UTI is not contagious but the bacteria which causes UTIs can travel between people during intercourse.
How to differentiate yeast infection and UTI?
A yeast infection usually occurs in vagina so the difference is in case of vaginal infection abnormal discharge and itching is noticed which is not in case of UTI.
Can a UTI cause bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer and urinary tract infections may have similar symptoms, but UTIs do not cause bladder cancer itself.
When should you seek medical help?
Seek medical help if you see blood in urine, you are pregnant or symptoms remain for many days.





